Figure 2.
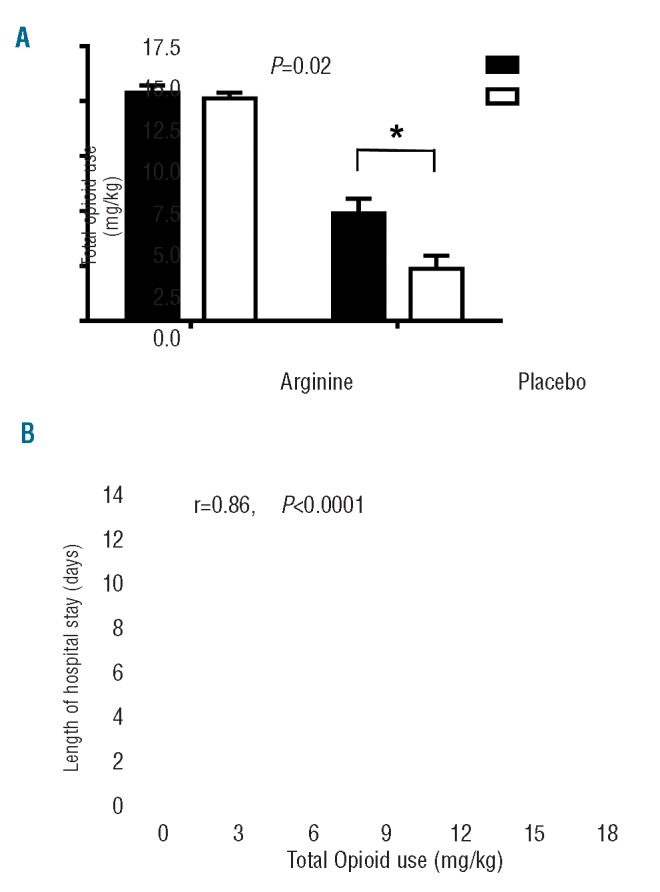
Impact of arginine therapy on total opioid use (mg/kg) and Pearson’s correlation between total opioid use (mg/kg) and total length of hospital stay (days). (A) Arginine supplementation (unfilled circles) led to a significant and clinically relevant reduction in total opioid use by 54% over the course of the hospital stay compared to total opioid use in the placebo group (filled circles). The difference remains significant even when the two outliers with the largest total opioid use in the placebo arm are excluded from the analysis (P=0.04). (B) Total opioid use (mg/kg) is directly correlated to length of hospital stay (r=0.86, P<0.0001).
