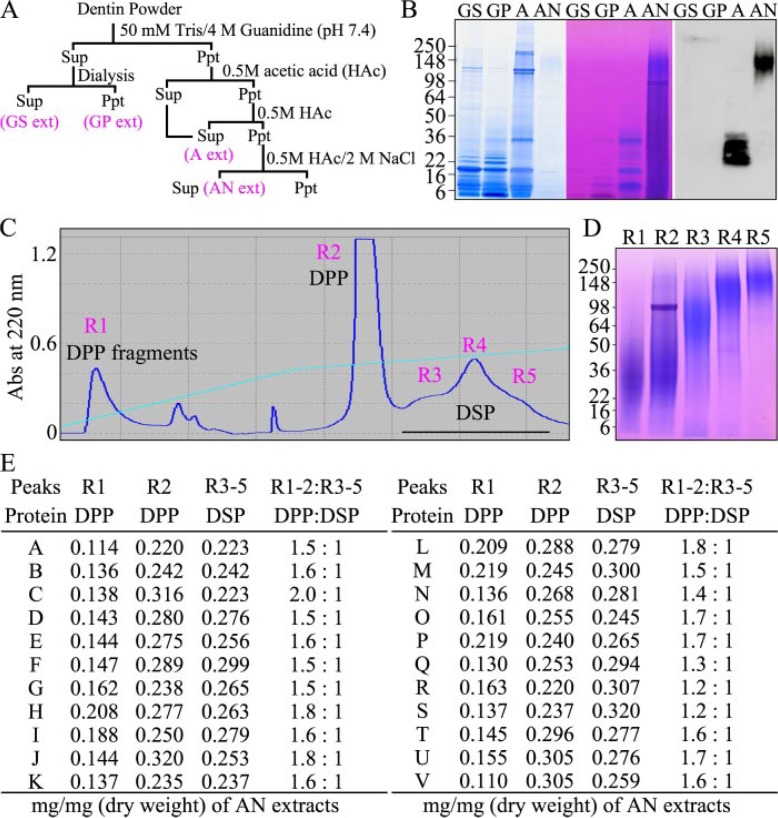
FIGURE 1.
Relative abundance of DSP and DPP in developing porcine molars. A, strategy for isolating dentin proteins from dentin powder that generates 4 extracts: the guanidine supernatant (GS extract), guanidine pellet (GP extract), acid extract (A extract), and acid/NaCl (AN extract). B, SDS-PAGE (4–20% gradient gel) stained with CBB (left), Stains-all (center), and a Western blot immunostained with an anti-DSP Ab (right). High molecular weight DSPP-derived proteins in the AN extract do not stain with CBB, but stain deeply with Stains-all. High molecular weight DSPP-derived proteins are in the AN extract are purified by size exclusion chromatography (not shown) followed by RP-HPLC. C, RP-HPLC chromatogram exhibits five peaks labeled R1 through R5. D, SDS-PAGE (4–20% gradient gel) stained with Stains-all shows DPP fragments (R1), intact DPP with DPP fragments (R2), DSP proteoglycan core (R3), DSP proteoglycan (R4), and DSP-DGP proteoglycan (R5). The weight of the AN extract and fractions R1 through R5 were measured for dentin obtained from each of 22 pigs (labeled A through V). E, table showing the dry weights of fractions R1, R2, and R3 through R5 divided by the total dry weight of the AN extract, and the dry weight of DPP (R1+R2) relative to DSP (R3–R5) in the AN extracts.