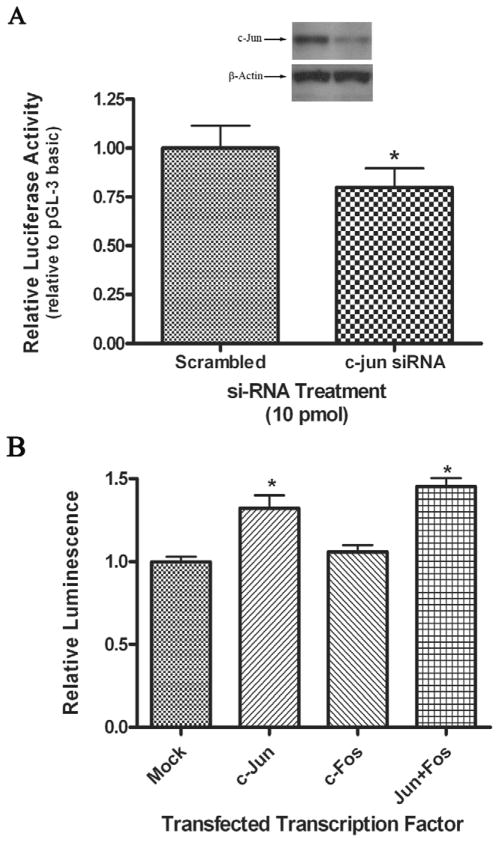
Figure 4. AP-1 is important for maximal human nCDase proximal promoter activity and sufficient to induce its activity.
A) HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with siRNA against c-Jun or scrambled siRNA and the PGL-200 luciferase reporter in DMEM containing FBS. fLuc activity was measured 24 h post-transfection and normalized to rLuc activity. The c-Jun siRNA-induced decrease in luciferase activity is expressed relative to the activity from scrambled siRNA-treated cells, where an asterisk marks a significantly different decrease in activity compared to scrambled siRNA treated cells. Results represent the mean ± S.E.M of at least three individual experiments. (A insert) Cell lysates were analyzed by western blots to determine c-Jun knockdown efficiency. Representative autoradiograph from Western analyses demonstrates the knockdown of c-Jun. Knockdown levels were quantified using Image J for densitometry analyses.) B) Overexpression of c-Jun indicated that AP-1 is sufficient to increase the activity of the human nCDase proximal promoter. HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with the PGL-200 luciferase reporter vector and either c-Jun expression vector, c-Fos expression vector, both c-Jun and c-Fos vectors, or empty vector. fLuc activity was measured 24 h post-transfection and normalized to rLuc activity. Reporter activity is expressed relative to the luciferase activity from cells co-transfected with the empty vector (Mock). Results represent the mean ± S.E.M of at least three individual experiments. Significant changes in relative expression are marked with an asterisk.