Figure 2.
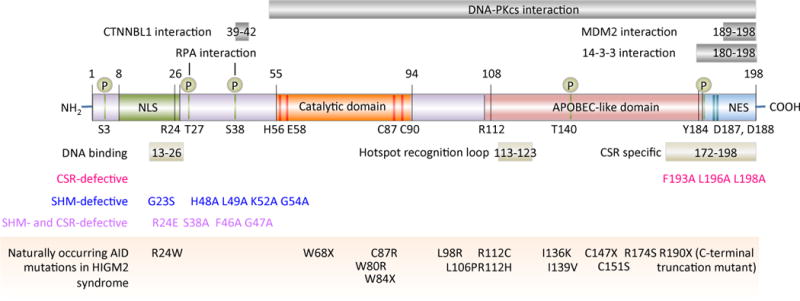
AID functional domains and functional altering mutations. The bottom panel showing the naturally occurring mutations in the AID gene that are responsible for the autosomal recessive disorder hyper-IgM syndrome type 2 (HIGM2). These mutations, as well as experimentally generated mutations in the AID gene, cause defects in CSR and/or SHM.
