Figure 1.
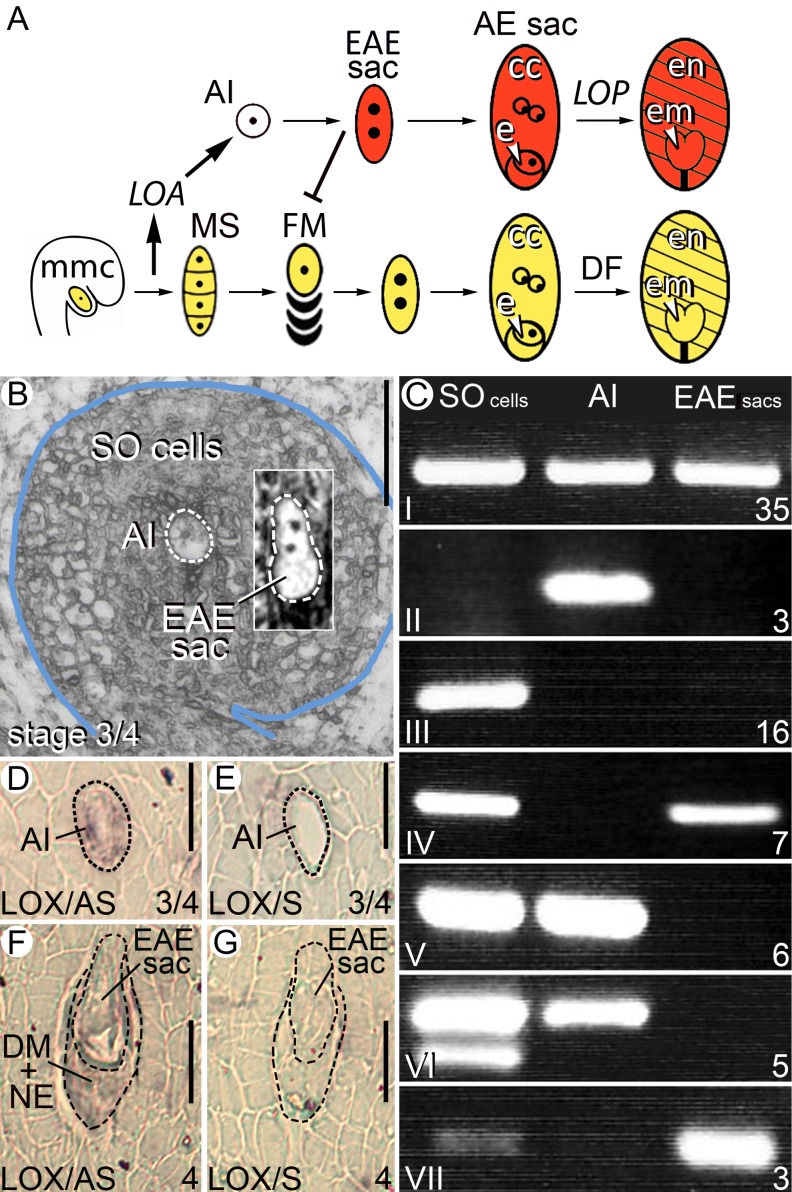
Sexual and apomictic pathways in H. praealtum, laser-captured cell types and analysis of gene expression. A, In apomictic H. praealtum, MMC meiosis and tetrad formation during sexual reproduction (yellow) activates the LOA locus leading to AI cell differentiation and EAE sac formation (red). Sexual development ceases in approximately 97% of ovules as the EAE sac displaces the sexual pathway generally at FM selection. A mature aposporous embryo sac develops with a diploid egg (e) and two diploid central cell (cc) nuclei. The LOP locus triggers fertilization-independent embryo (em) and endosperm (en) formation. Incomplete penetrance of LOA and LOP in approximately 3% of ovules results in haploid embryo sac formation, and double fertilization (DF) is required for seed initiation in gametophytes where LOP is lost by segregation. B, The three cell types isolated by LCM. Uninucleate AI cells and EAE sacs containing two to four nuclei were dissected in addition to SO cells collected from random locations in the ovule section. Bar = 50 µm. C, Seven classes of gene expression observed in the aRNA from the three laser-captured samples using RT-PCR to detect a suite of low-level-expressed ovary test genes. The number of genes in each class is indicated on the bottom right. D to G, In situ analysis in H. praealtum ovules of a LOX gene, one of three AI cell-expressed genes from class II in C. Antisense (AS) probes were used in D and F and control sense (S) probes in E and G. In situ analysis of the other two genes in H. praealtum and in sexual H. pilosella are shown in Supplemental Figure S3. Bar = 20 µm.