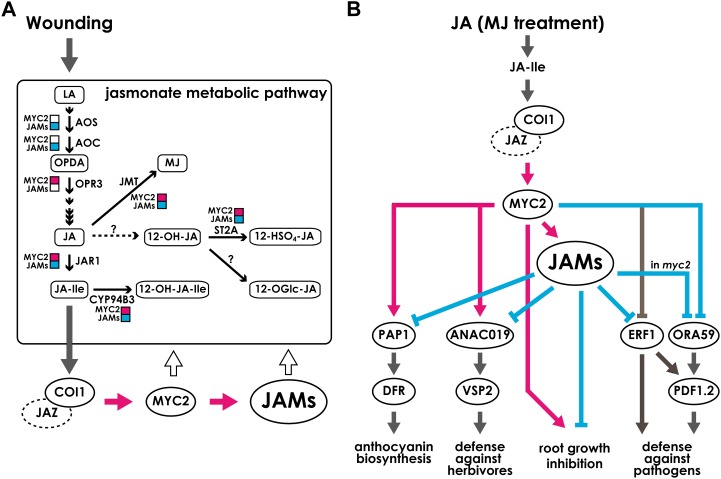
Figure 8.
Proposed models for the regulation of JA-responsive pathways by JAMs and MYC2. A, After wounding, synthesized JA-Ile activates jasmonate signaling. JAMs and MYC2 antagonistically regulated the jasmonate metabolic pathway in wounded leaves. It should be noted that effects on the expression of jasmonate biosynthetic and catabolic genes are shown, but those do not correlate with oxylipin levels. B, model of JAM-regulated transcription factors and metabolic enzymes during JA responses. After the recognition of JA-Ile by the COI1-JAZ complex, MYC2 is activated and regulates other transcription factors. JAMs also are targets of MYC2 and function in jasmonate signaling. JAMs negatively regulate the targets of MYC2. Note that the arrows show transcriptional regulation except for the arrows pointing to “root growth inhibition.” Pink arrows and squares represent positive effects shown experimentally in this paper. Pale blue arrows and squares represent negative effects shown experimentally in this paper. Black thin arrows represent metabolic reactions. Dark gray arrows are drawn based on previous reports. White arrows represent the feedback regulation by transcription factors. Note that the negative effect of JAMs on ORA59 expression was observed in the myc2 background. For abbreviations, see Figure 1.