Table 1. Screening of Iodination Conditionsa.
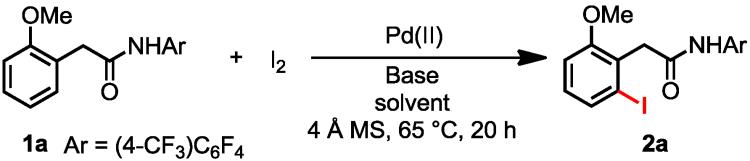
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| entry | Pd (II)b | basec | solventd | yield (%)e |
| 1 | Pd(OAc)2 | – | DMF | 15 |
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 | CsOAc | DMF | 62 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | CsOAc | t-AmylOH | <5 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 | CsOAc | DMF/t-AmylOH | 80 |
| 5 | Pd(OAc)2 | CsOAc/NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 99 |
| 6 | Pd(OAc)2 | NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 35 |
| 7g | Pd(OAc)2 | CsOAc/NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 98 (95%h) |
| 8 | – | CsOAc/NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 0 |
| 9 | PdCl2 | CsOAc/NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 83 |
| 10 | PdI2 | CsOAc/NaHCO3f | DMF/t-AmylOH | 75 |
| 11 | PdI2 | – | DMF/t-AmylOH | <5 |
The reactions were run on 0.10 mmol scale in a 25 mL-sealed tube under aira.
5 mol % of the Pd(II) catalyst was used unless otherwise stated.
1.2 eq of CsOAc was used.
Solvent volume = 2.0 mL; DMF/t-AmylOH = 1:1.
% yield was determined e by the 1H NMR spectroscopy using CH2Br2 as the internal standard.
1.0 eq of NaHCO3 was added.
The reaction was run on 0.30 mmol scale with 2 mol % Pd(OAc)2 in 5.0 mL of solvent.
Yield of the isolated product.
