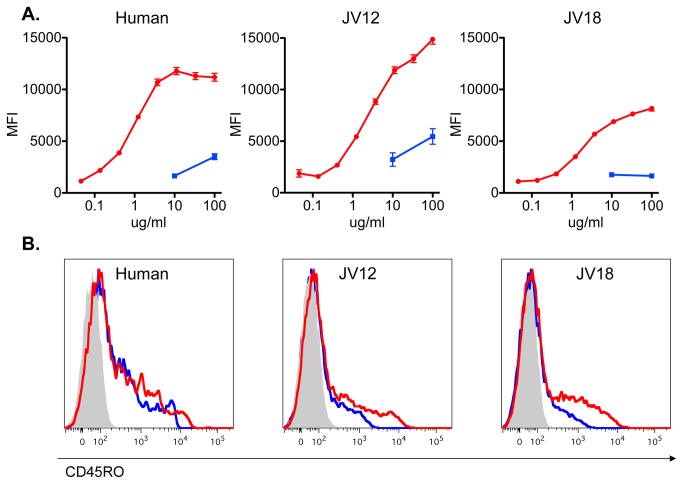
Figure 5. Relative avidity of UCHL1 for human and pigtailed macaque CD45RO.
A. Indirect immunofluorescence and flow cytometry were performed on human and 2 sets of pigtailed macaque (JV12 and JV18) PBMC. Equal numbers of thawed, rested PBMC were incubated with serial dilutions of UCHL1 before staining with an excess of Alexa-488 conjugated anti-mouse IgG. Acquired cells were gated on singlets and lymphocytes by light scatter. A gate for UCHL1 positive cells was then drawn. Data presented in red are the mean fluorescent intensity of the positive cells. Staining of cells by IgG2a isotype controls are shown in blue. Data representative of n=3 experiments. B. Human and pigtailed macaque (JV12 and JV18) PBMC were stained with biotinylated UCHL1 and streptavidin-PE in a direct or indirect staining method. For the direct method, biotinylated mAb was incubated with streptavidin-PE for twenty minutes before adding the multimeric complex (to a final concentration of 20µg/ml Ab and 2µg/ml streptavidin-PE) to the cells. For the indirect method, cells were first incubated with 20µg/ml of biotinylated mAb for thirty minutes, washed thoroughly and then incubated with 2µg/ml of streptavidin-PE. Acquired cells were gated on singlets and lymphocytes by light scatter. Direct immunofluorescence with multimeric UCHL1 is shown in red. Indirect immunofluorescence with monomeric UCHL1 is shown in blue. Autofluorescence of unstained PBMC is shown in grey. Data representative of a single experiment.