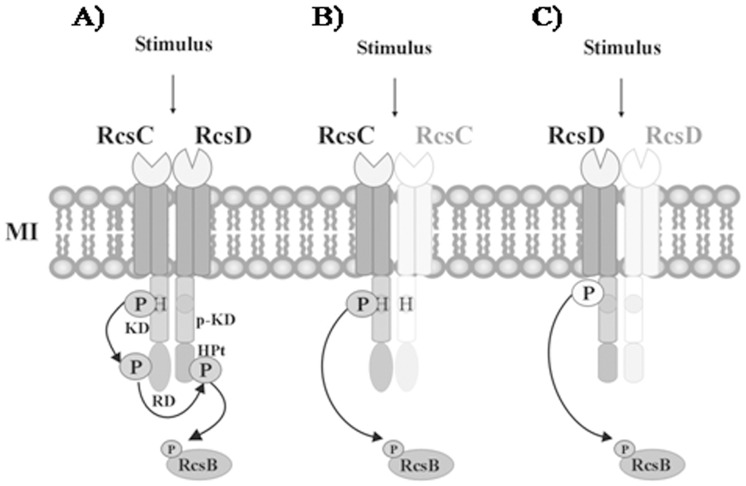
Figure 6. Signal transduction model of the RcsCDB phosphorelay system.
In response to cell envelop stress, the Rcs system activation can proceed at least in three pathways: (A) After that an specific stimulus is sensed by RcsC, this protein is autophosphorylated and able to interacts with RcsD, leading to the transfer of phosphate group to the RcsB regulator. The RcsB phosphorylated form is able to bind the promoter region of those target genes required to produce an instant response. (B) Same or different stimulus can produce the RcsC autophosphorylation forming a complex with other no phosphorylated RcsC monomer, and then the phosphate group is transferred to RcsB to modulate the gene expression. (C) In different growth condition, other stimulus could be recognized by RcsD, which after autophosphorylation interacts with other no phosphorylated-RcsD monomer. Then, the phosphate group is transferred to RcsB in order to regulate the expression of those genes necessary for bacteria adaptation. H, histidine; P, phosphate group; KD, kinase domain; p-KD, pseudo kinase domain; RD, receiver domain; HPt, histidine phosphotransfer domain.