Figure 3.
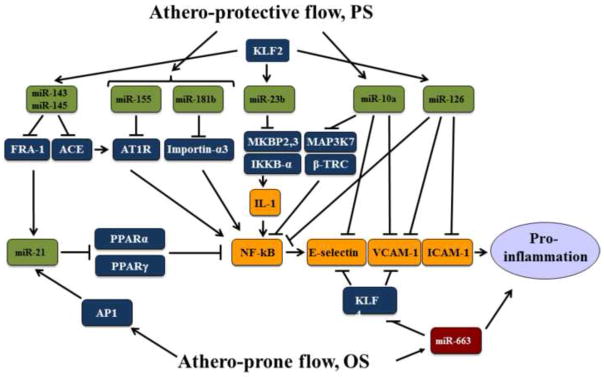
Putative miR network that regulates the pro-inflammatory NF- B pathway. PS activates the indicated miRs that result in the inhibition of NF- B by direct targeting and indirect regulation. Additionally, miR-10a and miR-126 directly inhibit the expression of E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1. KLF2 plays a major role in transactivating many of the anti-inflammatory miRs, including miR-143, miR-145, miR-23b, and miR-126. In contrast, OS causes AP-1 activation and the consequent miR-21 induction. miR-21 inhibits PPARα and PPARγ, both negatively regulate NF-κB. OS also up-regulates miR-663 that targets KLF4 and therefore desuppresses E-selectin and VCAM-1. The overall outcome of this intricate network under OS is pro-inflammation.
