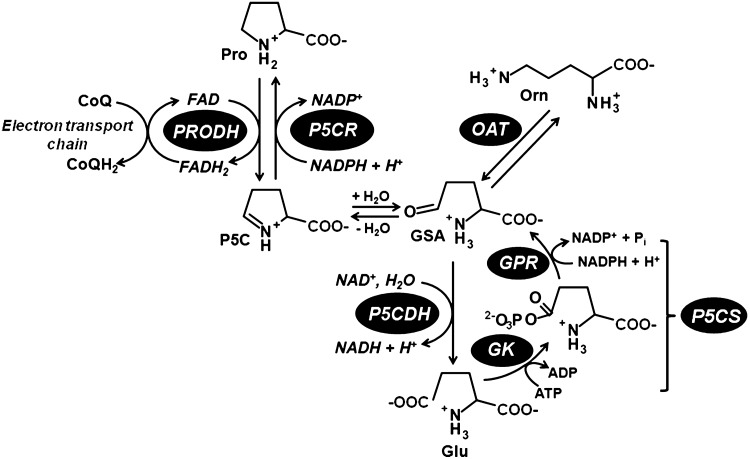
FIG. 1.
Reactions of the proline metabolic pathway. Proline (Pro) is synthesized from glutamate (Glu) starting with the enzymes glutamate kinase (GK) and γ-glutamyl phosphate reductase (GPR), which in plants and animals are fused together in the bifunctional enzyme P5C synthetase (P5CS). The intermediate, γ-glutamate-semialdehyde (GSA), spontaneously cyclizes to Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C), which is then reduced to proline by P5C reductase (P5CR). Alternatively, GSA/P5C can be generated from ornithine and ornithine-δ-aminotransferase (OAT). Proline is oxidized back to glutamate by proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) and P5C dehydrogenase (P5CDH) in the mitochondrion. PRODH couples proline oxidation to the reduction of ubiquinone (CoQ) in the electron transport chain (ETC). In Gram-negative bacteria, PRODH and P5CDH domains are fused together in the PutA protein.