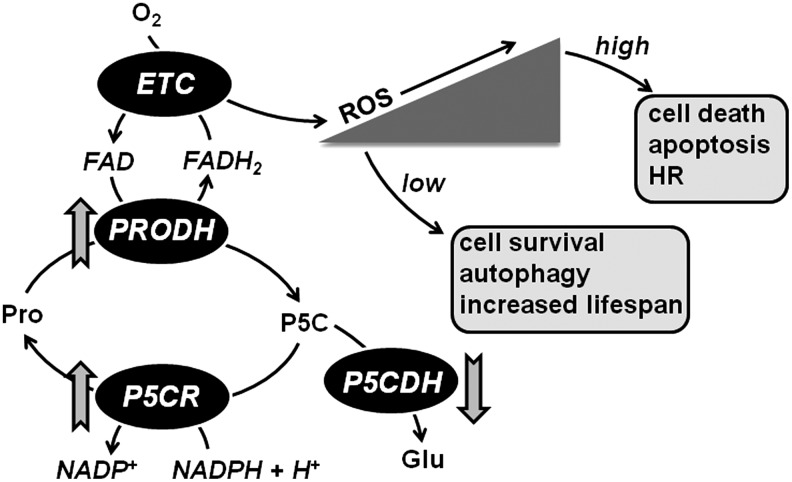
FIG. 6.
Proline metabolism and ROS formation. PRODH activity leads to ROS formation in mitochondria by coupling proline oxidation to reduction of the ETC. Increases in PRODH and P5CR activities along with down-regulation of P5CDH are predicted to increase proline-P5C cycling and ROS levels. ROS levels flucuate according to changes in proline metabolism and activate diverse signaling pathways, thereby enabling proline to influence different cellular processes.