Abstract
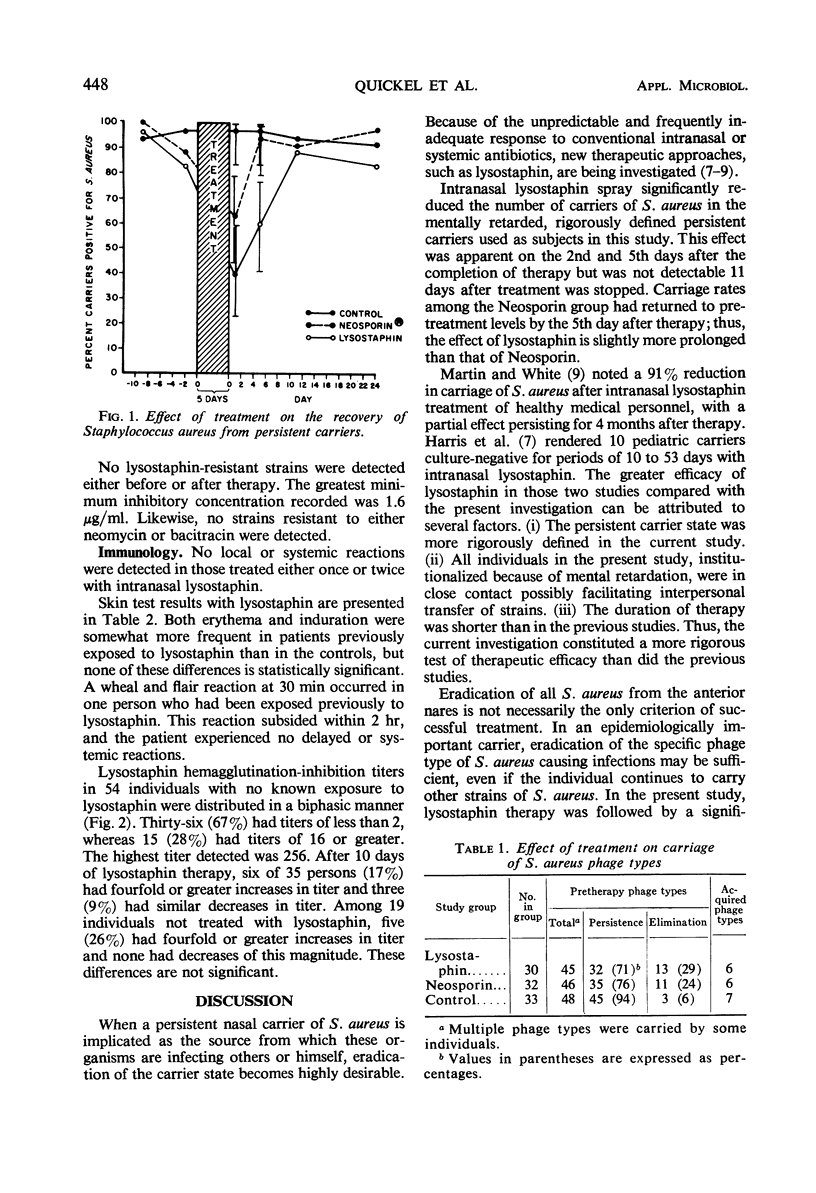
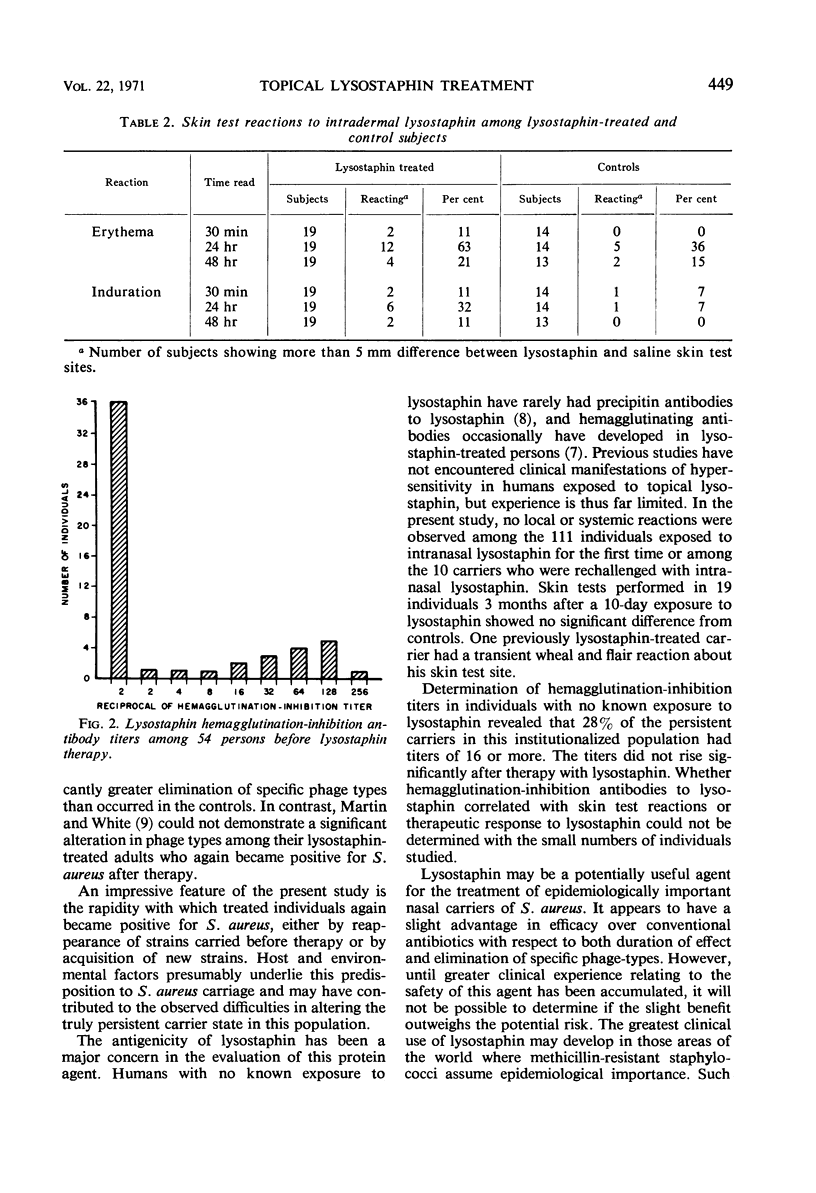
The efficacy of lysostaphin nasal spray and Neosporin ointment (Burroughs Wellcome & Co.) in altering nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus was studied with persistent carriers in an institution for mentally retarded children and adults. Treatment for 5 days with either agent significantly reduced carriage rates. This effect persisted through the 5th day after therapy with lysostaphin but not with Neosporin. By the 11th day after therapy, carriage rates in the treatment and control groups were not significantly different. Except for a single immediate wheal and flair skin test reaction, no other evidence of adverse reactions to topical lysostaphin was detected. No consistent changes in hemagglutination-inhibition titers to lysostaphin were observed after therapy. Lysostaphin appears to be slightly more effective than conventional topical antimicrobial therapy in reducing nasal carriage of staphylococci in this rigorously defined population of persistent carriers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWDER H. P., ZYGMUNT W. A., YOUNG J. R., TAVORMINA P. A. LYSOSTAPHIN: ENZYMATIC MODE OF ACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 23;19:383–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett F. F., McGehee R. F., Jr, Finland M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at Boston City Hospital. Bacteriologic and epidemiologic observations. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 29;279(9):441–448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808292790901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROPP C. B., HARRISON E. F. THE IN VITRO EFFECT OF LYSOSTAPHIN ON CLINICAL ISOLATES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Dec;10:823–828. doi: 10.1139/m64-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. E., Goodman J. S., Koenig M. G. Lysostaphin: an enzymatic approach to staphylococcal disease. 3. Combined lysostaphin-methicillin therapy of established staphylococcal abscesses in mice. Yale J Biol Med. 1968 Aug;41(1):62–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. M., DeFranco J. M., Watanakunakorn C., Hamburger M. Studies in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis in dogs. VI. Treatment with lysostaphin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. L., Nunnery A. W., Riley H. D., Jr Effect of lysostaphin on staphylococcal carriage in infants and children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:110–112. doi: 10.1128/AAC.7.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., White A. The reacquisition of staphylococci by treated carriers: a demonstration of bacterial interference. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):791–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., White A. The selective activity of lysostaphin in vivo. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jul;70(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. LYSOSTAPHIN: A NEW BACTERIOLYTIC AGENT FOR THE STAPHYLOCOCCUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:414–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF LYSOSTAPHIN--A LYTIC AGENT FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Melly M. A., Hash J. H., Koenig M. G. Lysostaphin: an enzymatic approach to staphylococcal disease. I. In vitro studies. Yale J Biol Med. 1967 Feb;39(4):215–229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Melly M. A., Koenig M. G. Lysostaphin: an enzymatic approach to staphylococcal disease. II. In vivo studies. Yale J Biol Med. 1967 Feb;39(4):230–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt W. A., Harrison E. F., Browder H. P., Tavormina P. A. Comparative inhibition of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus by lysostaphin and other antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Aug;16(8):1174–1178. doi: 10.1128/am.16.8.1174-1178.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


