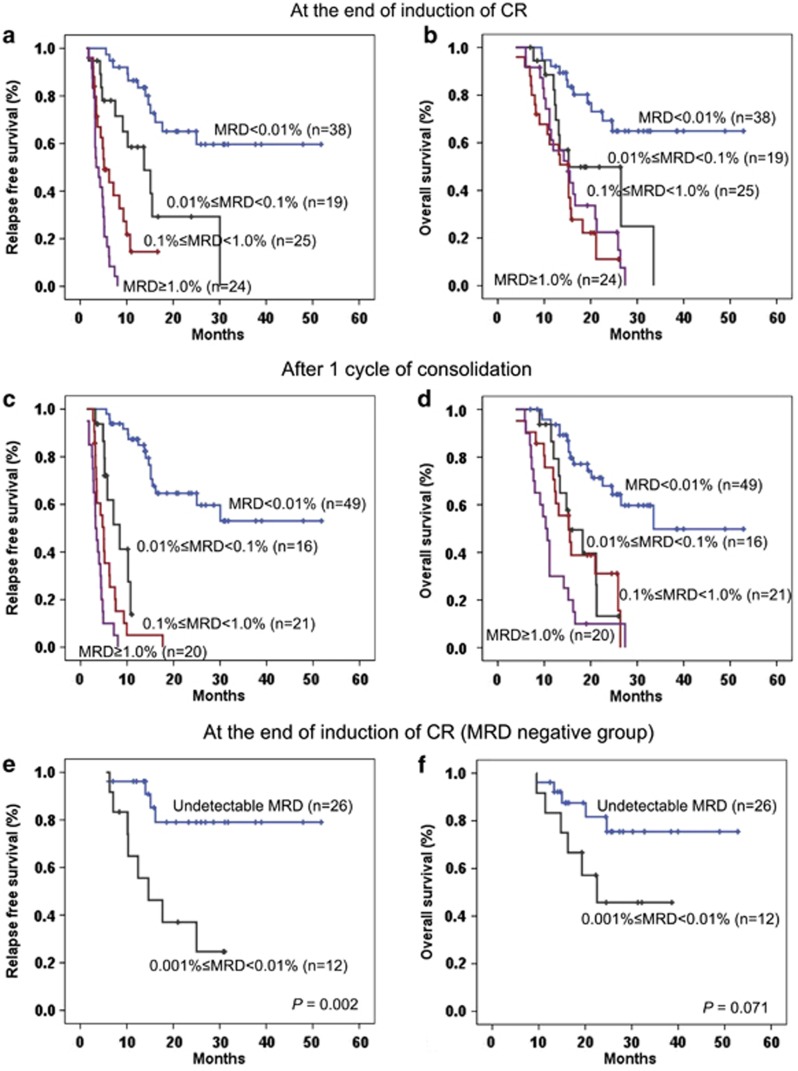
Figure 3.
The 2-year RFS and OS in 106 adult patients with B-ALL according to immunophenotypic MRD level at the end of induction of CR and after one consolidation. (a) The RFS of the patients with negative and positive MRD status at the end of induction of CR were 65.1±8.7% and 12.3±5.1%, respectively (P<0.001). In parallel, the RFS of the patients with low and intermediate burden of MRD were 29.3±13.4% and 14.5±8.6% however, the patients with high burden of MRD all relapsed (low vs intermediate, P=0.014; and intermediate vs high, P=0.004). (b) The estimated 2-year OS of the patients with negative and positive MRD status at the end of induction of CR were 69.2±8.3% and 25.0±6.2%, respectively (P<0.001). No statistical significance was observed in the three groups with a 2-year estimated OS rate of 49.8±12.7, 11.0±9.0 and 22.4±9.3%, respectively (low vs intermediate, P=0.070; and intermediate vs high, P=0.411). (c) The 2-year RFS of the patients with negative MRD status after one consolidation were 64.6±7.8%, and no patients with positive MRD status were relapse-free (P<0.001). (d) The estimated 2-year OS of the patients with negative and positive MRD status after one consolidation were 67.9±7.5% and 18.9±6.2%, respectively (P<0.001). There was no significance between the three groups in MRD-positive status: Low, 13.2±11.7% Intermediate, 31.1±11.3% and High, 10.0±6.7% (low vs intermediate, P=0.859; and intermediate vs high, P=0.056). (e) The 2-year RFS of the patients with MRD 0.001% to <0.01% and those with undetectable MRD at the end of induction of CR (n=38) were 37.0±14.6% and 79.1±9.5%, respectively (P=0.002). (f) Patients with undetectable MRD had a better 2-year OS than those with MRD 0.001% to <0.01% at the end of induction of CR (81.7±8.5% and 45.7±15.5%, respectively, P=0.071), but no statistical significance was observed.