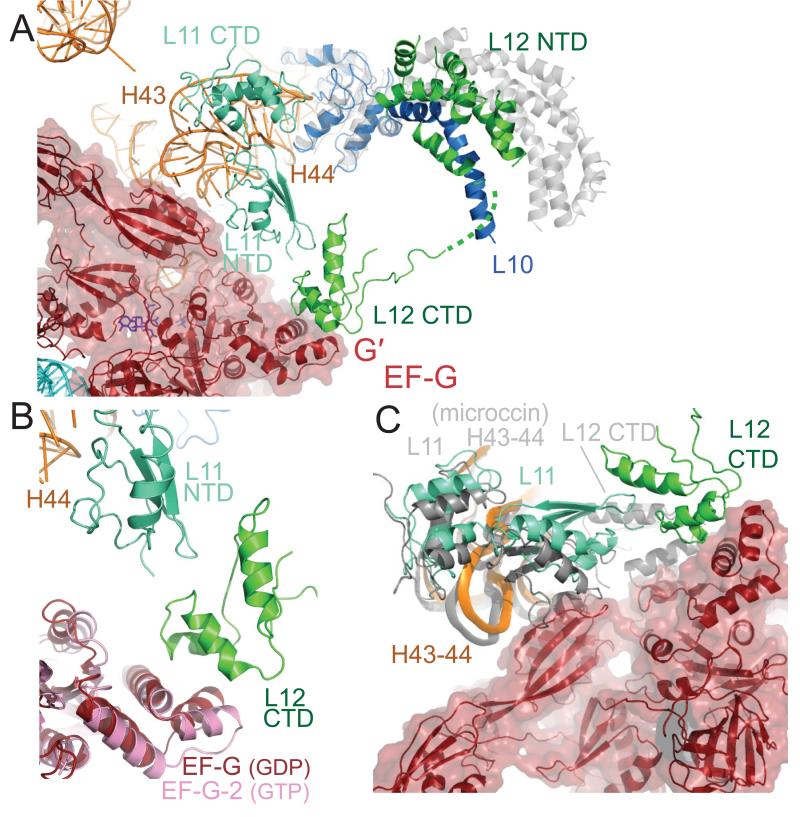
Figure 6.
Interaction of EF-G with the L11 region and the L10-L12 stalk. A. Overview showing that EF-G interacts directly with the L11 RNA (helices 43 and 44) through domain V. The L10-L12 stalk has bent towards the L11 region relative to the structure of the isolated stalk (gray) (37) as judged by superimposing the globular part of L10. As a result, a copy of the CTD of L12 bridges the G′ domain of EF-G and the NTD of L11 by interacting with both of them. B. Conformational changes in the G′ domain and domain V of EF-G in the GDP-fusidic acid form in the ribosome (reddish-brown) as compared to the GTP form (pink) (13). C. Comparison of the structure of EF-G trapped in the post-translocational state of the ribosome with the structure of the 50S subunit bound to micrococcin (43). Domain V of EF-G interacts with helices 43 and 44 of 23S RNA that bind L11. A superposition of the micrococcin-bound 50S structure (gray) using all of 23S RNA shows that helices 43 and 44 (gray) superimpose reasonably well on the EF-G ribosome complex, but the NTD of L11 would clash with domain V of EF-G. The CTD of L12 is in the micrococcin-bound 50S structure is also in a very different location and orientation compared to the current structure where it interacts with the G′ domain.