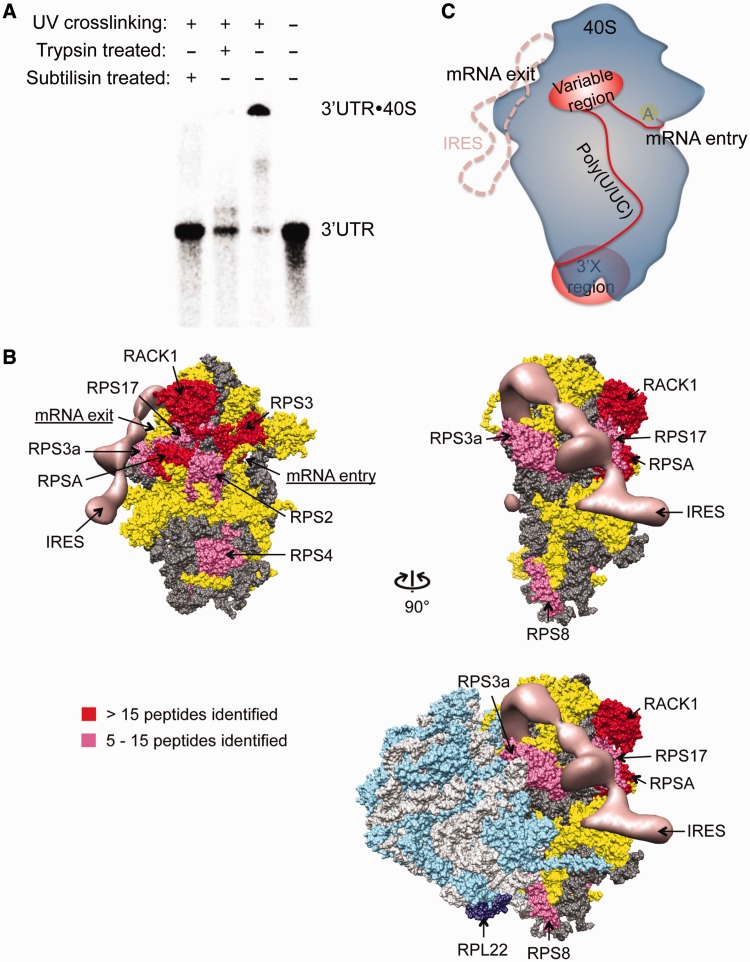
Figure 4.
Mapping of the 3′UTR interacting region on the 40S subunit. (A). Non-specifically cross-linked 3′UTR-40S complex can be degraded to the 3′UTR RNA alone by both trypsin and subtilisin. (B). Mapping result from 4-thiouridine mediated cross-linking of the 3′UTR to the 40S subunit. The hits were categorized based on the total number of spectra observed. Proteins with >15 spectra identified are assigned as strong binders (red), whereas those with between 5 and 15 spectra are assigned as moderate binders (magenta). Entries with four or less spectra are considered background noise from non-specific cross-linking. The HCV IRES is shown in salmon. In dark and light gray are ribosomal RNAs of the 40S and the 60S subunit, respectively. In yellow are the 40S ribosomal proteins not interacting with the 3′UTR. In cyan and dark purple are the 60S ribosomal proteins with RPL22 labeled in dark purple, which was indicated to interact with the 3′X region (34). All the 3′UTR interacting ribosomal/ribosome associated proteins are labeled. (C). Binding model for the HCV 3′UTR and the 40S ribosome. In blue is the 40S subunit, with position of the A site indicated by the yellow oval. In red is the 3′UTR with the variable and the 3′X region shown in oval and the poly(U/UC) tract as well as the linker between the stop codon and the beginning of the variable region stem-loop shown as curved lines. The HCV IRES-binding position on the 40S ribosome is shown in salmon dash line.