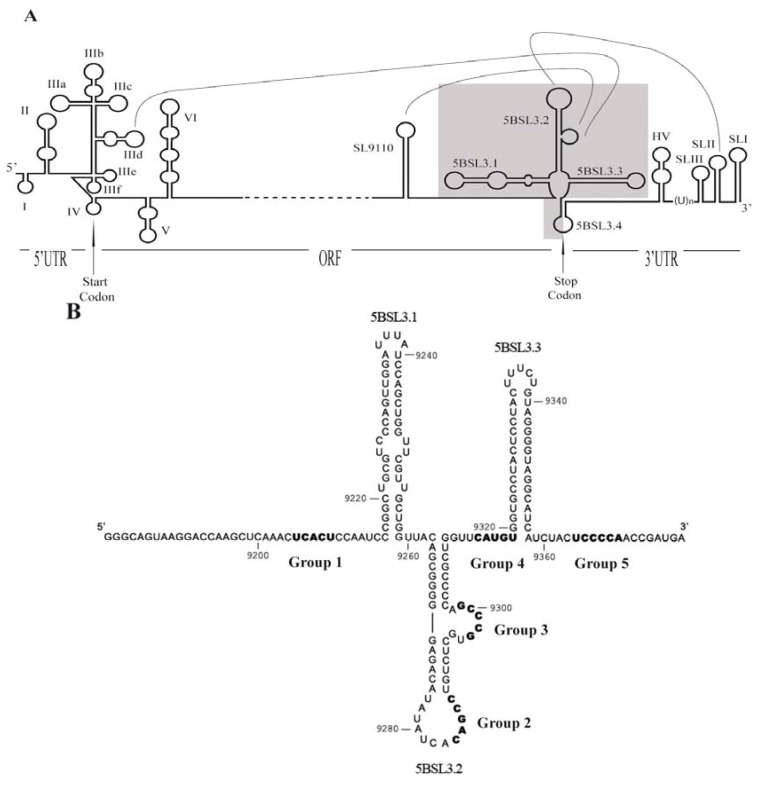
Figure 1.
(A) Diagram of the secondary structural elements of the 5' and 3' ends of the HCV genome. ORF indicates the only open reading frame, which is flanked by the 5' and 3' untranslatable regions (UTR). The translation start and stop codons are indicated by an arrow. The main structural domains at the 5' end are numbered I to VI; subdomains are identified by adding a lower case letter (IIIa–IIIf). The representation of the 3' part of the genome includes (from the 3' end): The 3' X-tail region that includes the SLI, SLII and SLIII domains; the polyU stretch [(U)n]; the hypervariable region (HV); the CRE domain, which includes domains 5BSL3.1, 5BSL3.2 and 5BSL3.3 at the 3' end of the coding region; and the stem-loop SL9110. Long range RNA-RNA interactions are depicted by lines. The genomic fragment used as a target for the in vitro selection procedure is shaded in the diagram; (B) The sequence and secondary structure for the HCV-CRE194 genomic RNA fragment used as target. Numbering refers to the nucleotides positions of the HCV Con1 isolate [33]. Motifs complementary to the consensus sequences of the groups of selected aptamer are shown in bold.