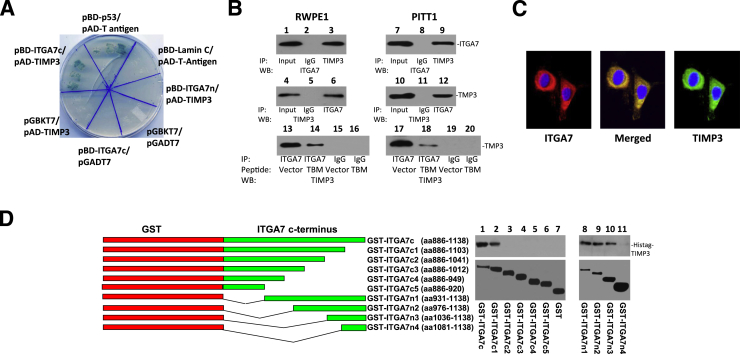
Figure 1.
ITGA7 binds TIMP3. A: β-Galactosidase activity of yeast harboring pBD-ITGA7c (amino acids 982 to 1138) and pAD-TIMP3, pBD-p53, and pAD-T antigen (positive control), or pBD-ITGA7n (amino acids 2 to 986) and pAD-TIMP3 or pBD-ITGA7c and pGADT7, or pGBKT7 and pAD-TIMP3, or pGBKT7 and pGADT7, or pBD-Lamin C and pAD-T antigen. B: Co-IP of ITGA7 and TIMP3. Proteins were extracted from RWPE1 and induced PITT1 cells (pCDNA4-ITGA7/pCDNA6TO transfected PC3 clone). The lysates were IP with the indicated antibodies and detected by Western blot (WB) analysis with either ITGA7 or TIMP3 antibodies. Lanes 13 to 20: RWPE1- or tetracycline-induced PITT1 cells were transfected with pCMV-FLAG or pCMV-TBM-FLAG (TIMP3 binding motif-FLAG). Immunoprecipitations and Western blot analyses were performed using the indicated antibodies. C: ITGA7 and TIMP3 colocalized in RWPE1. Immunostaining was performed using antibodies specific for ITGA7 or TIMP3, as described in Materials and Methods. Original magnification, ×20. D: ITGA7 binds with TIMP3 in vitro. Left panel: Diagrams of GST-ITGA7c mutants. Top right panel: Binding of GST-ITGA7c fusion proteins and its mutants with purified Histag-TIMP3 from bacterial extracts. After extensive washes, the bound proteins were eluted and immunoblotted with anti-TIMP3 antibodies. Bottom right panel: Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining of fusion proteins.