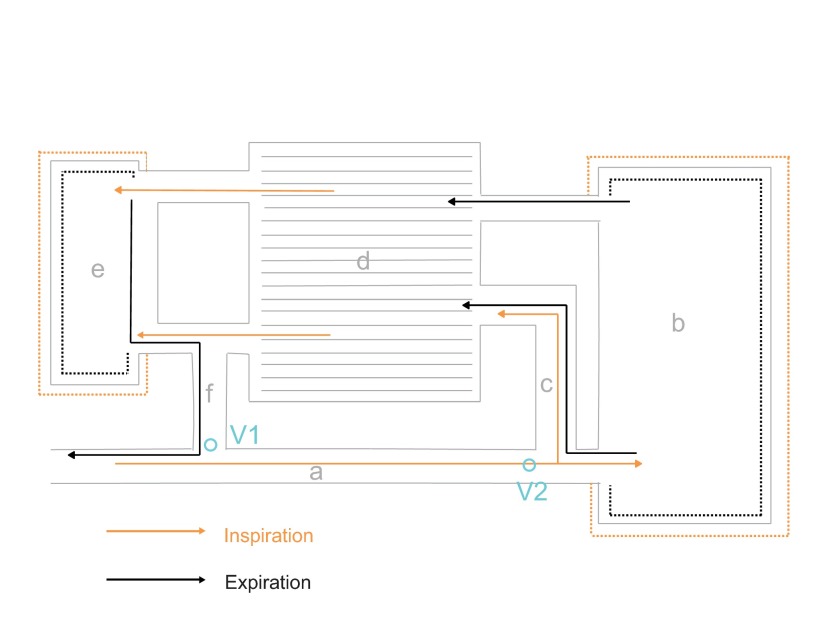
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the avian respiratory system illustrating the model for ventilation of the air sac system and lung. During inspiration (orange arrows), air is thought to flow through the mesobronchus (a) toward the posterior set of air sacs (b), bypassing the opening of the medioventral secondary bronchus (f), which connects to the anterior set of air sacs (e). A portion of air is thought to enter the lung (d) directly through the mediodorsal secondary bronchus (c). An ‘inspiratory aerodynamic’ valve (V1) is thought to regulate this inspiratory flow pattern. On expiration (black arrows), air moves from the posterior air sac system into the lung. A second aerodynamic valve (V2) is thought to prevent outflow through the mesobronchus. At the same time, air from the anterior set of air sacs is moved into the extrapulmonary primary bronchi and is exhaled through the trachea.