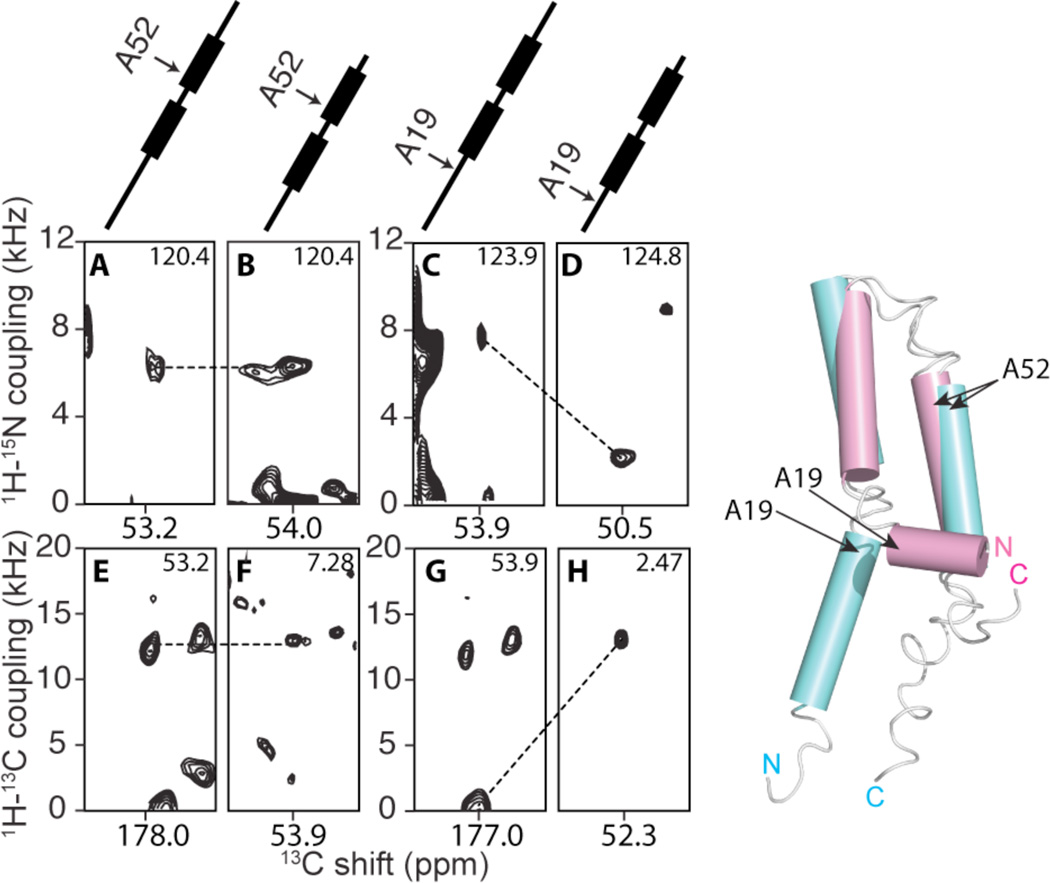
FIGURE 3.
Left: Observed changes in orientationally dependent frequencies demonstrate drastic changes in the structure of MerF caused by truncation of residues at the N-terminus. At the top are schematic drawings of the MerF secondary structure (thicker lines are trans-membrane helices) marked with the positions of the residues contributing to the signals. A, C, E and G are slices from spectra of MerF. B, D, F and H are slices from spectra of MerFt. The left panels (A, B, E and F) are from Ala52 located in the second trans-membrane helix. Both the 1H-15N and 1H-13C DCs of Ala52 are very similar for the full-length and truncated proteins. The right panels (C, D, G and H) are from Ala19, located in the N-terminal region, where the conformational change occurs and consequently large changes in DC values are observed. All slices are extracted from three-dimensional spectra at the noted values of the third dimension. Right: The structure of the truncated 60-residue protein (magenta) is superimposed on the structure of the full-length 81-residue protein (aqua).