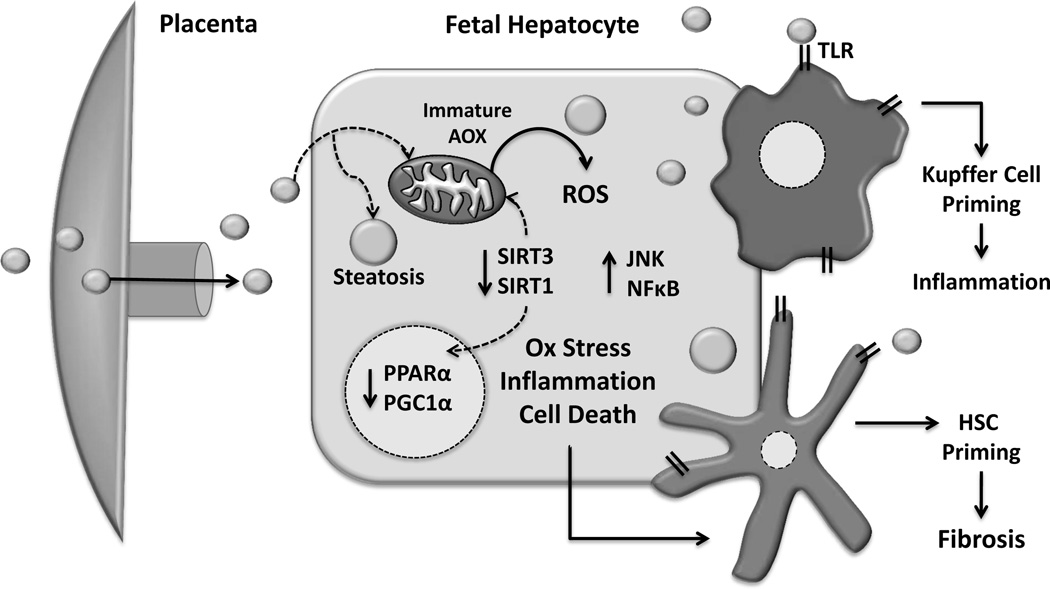
Figure 1. In utero lipid excess and hepatocyte maladaptive changes.
Increased lipid flux to the developing fetal liver establishes a lipotoxic environment characterized by oxidative stress, increased inflammation, cell death, and consequent dysregulation in oxidative metabolism genes. Additionally, Kupffer cell and hepatic stellate cell (HSC) pro-inflammatory priming by hepatocellular stress as well as direct stimulation by circulating lipids may also increase susceptibility to later disease. Antioxidant enzymes (AOX), Reactive Oxidative Species (ROS), Sirtuin 1 and 3 (SIRT1 and SIRT3), Toll-like receptors (TLR).