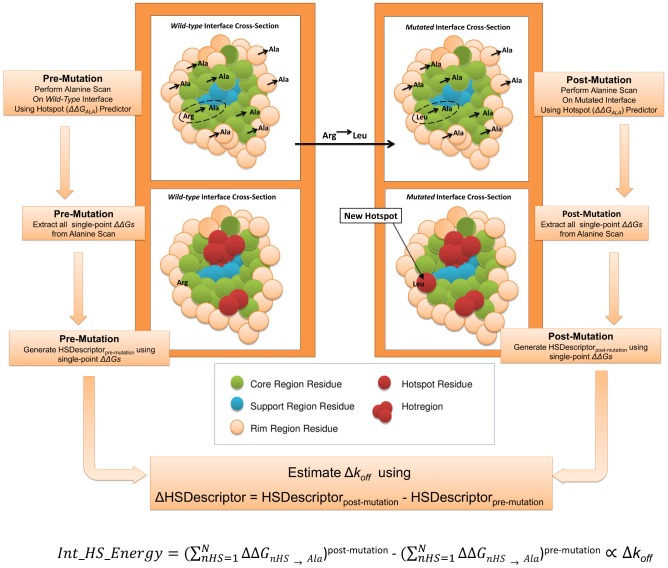
Figure 1. Off-rate estimation using hotspot energies and organization.
In this work we generate a set of hotspot descriptors for characterizing off-rate changes upon mutation. The hotspot descriptors use single-point alanine ΔΔGs from computational alanine-scans generated using hotspot prediction algorithms, to predict changes in off-rate upon single-point and multi-point mutations to all residue types. To do so, for a given wild-type complex structure, the interface is scanned for hotspots using a hotspot prediction algorithm. The single-point alanine ΔΔGs from the scan are extracted and stored. Next, the structural mutation in question is applied and the mutated interface re-scanned for hotspots. This generates a new set of single-point alanine ΔΔGs for the mutated interface. Note that the mutation in question may also affect the hotspot energies of other neighboring residues which are not mutated. The two sets of ΔΔGs are then used to generate a set of hotspot descriptors, where the final hotspot descriptor value is the change in the descriptor's value from mutant to wild-type. For example in the case of Int_HS_Energy, the final value is the change in the sum of the ΔΔGs, of all hotspot residues, pre- and post-mutation. Hotspots are also categorized into core, rim, support and hotregions. This enables us to investigate and account for cooperative effects within hotregions and to identify differences in regions critical for stability, both on complexes of different size and interface area.