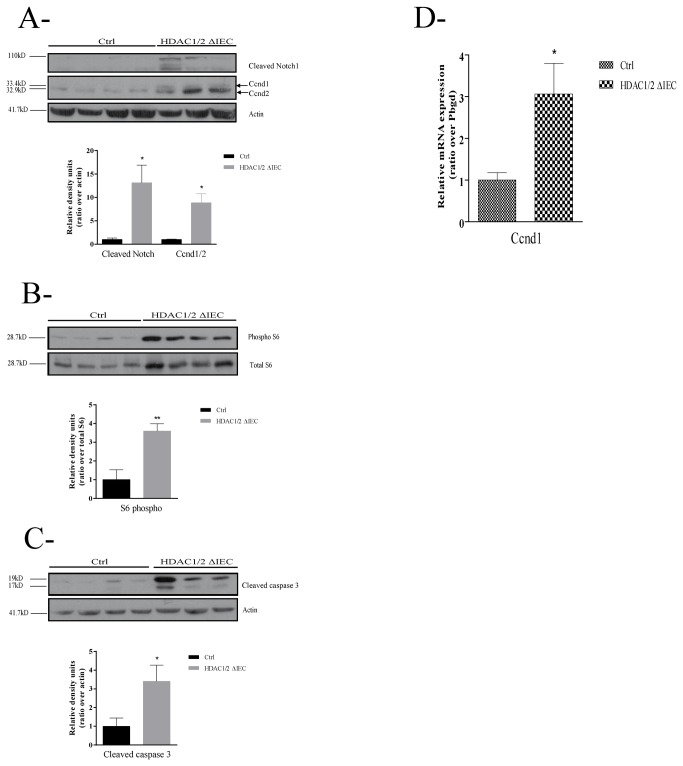
Figure 5. Conditional intestinal epithelial HDAC1/2 loss leads to altered activation of cell homeostasis regulators.
Total protein extracts from three to four one-year-old control (Ctrl) or conditional intestinal epithelial HDAC1/2 (HDAC1/2ΔIEC) colons were separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane and analysed by Western blot for expression of (A) Cyclin D (Ccnd1, MW: 33.4 kD; Ccnd2, MW: 32.9 kD), cleaved Notch1 (MW: 110 kD) and actin (MW: 41.7 kD) as a loading control; (B) phosphorylated and total ribosomal protein S6 (MW: 28.7 kD); (C) cleaved caspase 3 (MW: 17 kD), with actin as a loading control. The histograms indicate the ratio of band intensities normalized to actin (A, C) or total ribosomal protein S6 (B). Quantification of band intensity was performed with the Quantity One software. Results represent the mean ± SEM (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01). D. Cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) increased expression was confirmed by qPCR analysis of total RNAs isolated from control or conditional intestinal epithelial HDAC1/2 colons. Results represent the mean ± SEM (*p≤0.05).