Figure 1.
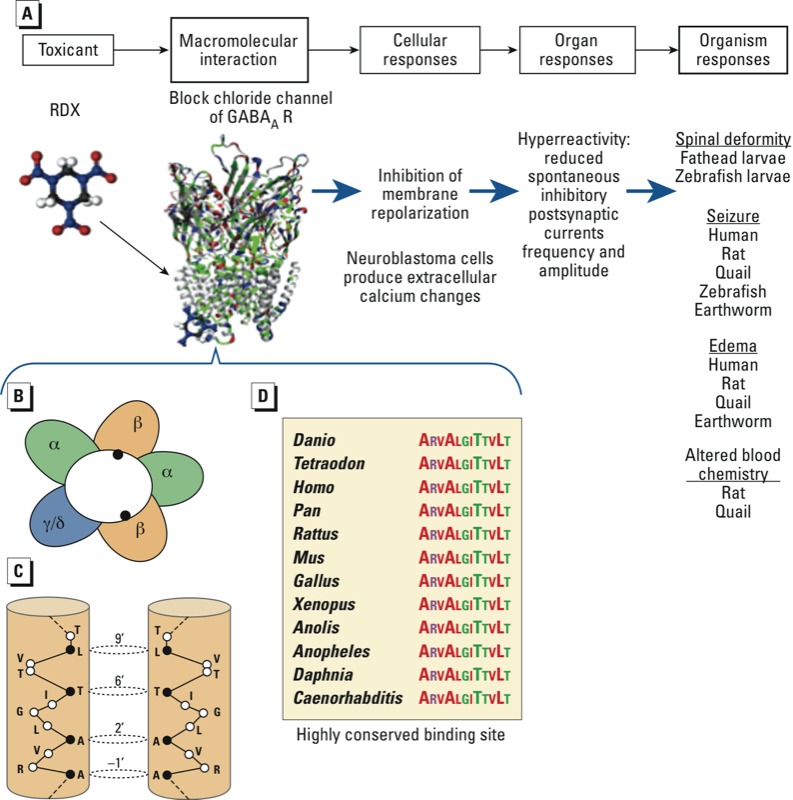
Cross-species similarity of GABAA receptor (GABAAR) and RDX toxicity in an AOP framework. (A) Schematic of pathway. (B) Schematic view of a GABAAR heteropentamer with the channel in the center formed of two copies of an α subunit (α1–α6), two copies of a β subunit (β1, β2, or β3), and a third subunit of γ or δ protein (adapted from Olsen 2006). (C) Cytoplasmic end of the transmembrane channel for two β-3 subunits, indicated by closed circles in (B) in GABAAR, showing the residues that form the binding site for picrotoxin (PTX) and RDX [closed circles in (C): residues numbered 1’–23’ from the N-terminal bottom; open circles represent residues that are not part of the binding site]. (D) Sequence alignment of the PTX/RDX binding site for several species: Danio rerio, Tetraodon nigroviridis, Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Rattus norvegicus, Mus musculus, Gallus gallus, Xenopus tropicalis, Anolis carolinensis, Anopheles gambiae, Daphnia pulex, and Caenorhabditis elegans.
