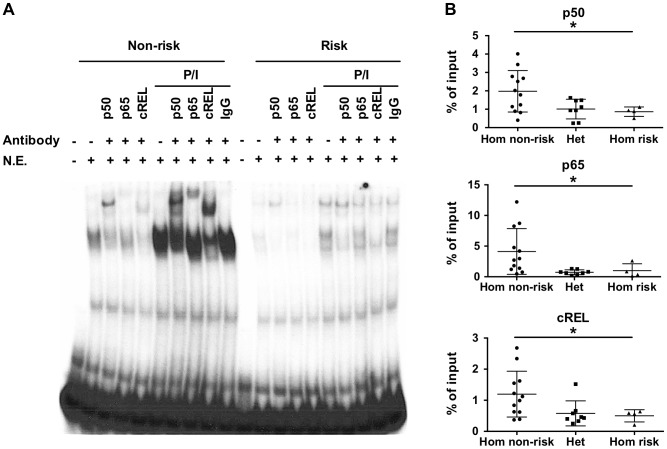
Figure 1. The TT>A variants result in reduced binding of a nuclear protein complex that contains NF-κB subunits.
a. EMSA was performed with radiolabeled nucleotides containing the non-risk (TT) (40 bp) and risk (-A) (39 bp) polymorphisms. Nuclear extracts were derived from EBV transformed B cell lines at rest or stimulated with P/I and in the presence or absence of the indicated NF-κB subunit antibodies. Rabbit IgG was used as the isotype control. N.E. -nuclear extracts. b. ChIP-pPCR was performed using EBV transformed B cell lines (-A/-A = 4; TT/-A = 8; TT/TT = 12) stimulated with P/I. ChIP was performed with antibodies specific against NF-κB p50, p65, and cRel subunits, followed by qPCR with primers neighboring TT>A polymorphic region. Statistical comparisons were made using one-way ANOVA, * indicates p<0.05.