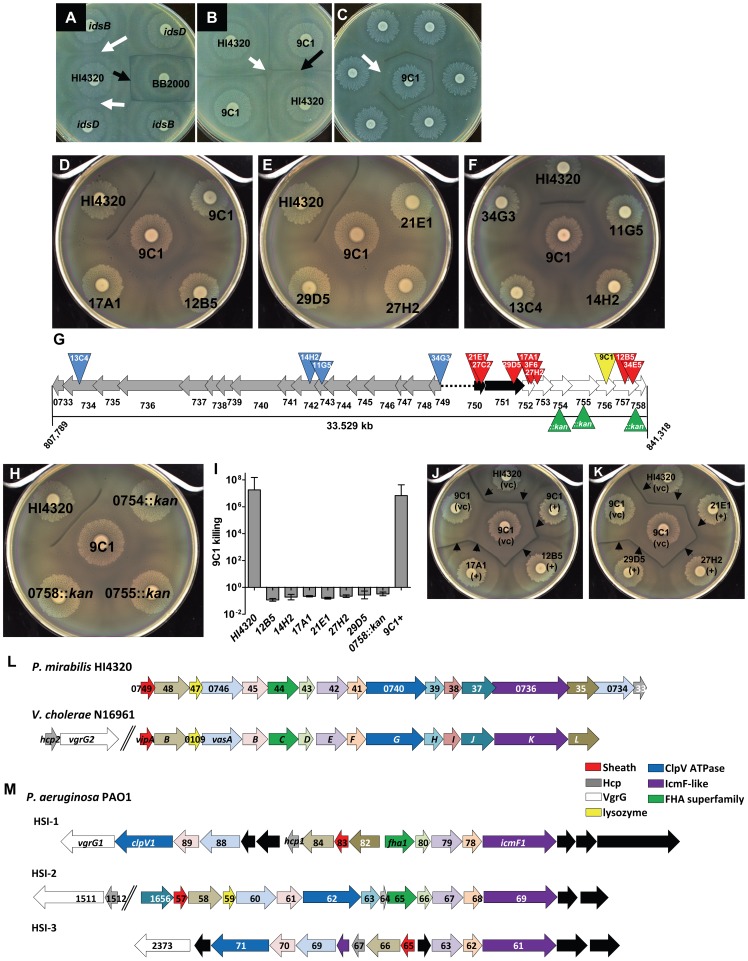
Figure 1. Social recognition and Dienes line formation results from bacterial killing, dependent on the T6SS and divergent hcp-vgrG effector operon.
(A) Non-identical P. mirabilis strains, BB2000 and HI4320, form a Dienes line (black arrow). Mutations within idsB and idsD of HI4320 do not form a Dienes line with their parental strain (white arrows). (B) One of 1,920 HI4320 Tn5 insertion mutants, identified as 9C1, formed a Dienes line (black arrow) with its parental strain. HI4320 merges with itself at the center of the plate (white arrow). (C) Transposon mutants were rescreened against 9C1 to find mutants that lost the ability to form a Dienes line (arrow). (D, E) Mutant 9C1 merged with itself and insertion mutants 12B5, 17A1, 21E1, 27H2, and 29D5. (F) 9C1 merges with T6SS mutants 11G5, 14H2, 13C4, and 34G3. (G) Transposon insertions (red triangles) in genes located within the same operon as the 9C1 mutant (yellow triangle). The three genes not identified in the genetic screen were disrupted by targeted insertion of antibiotic resistance gene (green triangles). hcp and vgrG homologs (black arrows) and additional genes predicted to encode effectors delivered by the T6SS (white arrows) are indicated. Additional mutants (13C4, 14H2, 11G5, and 34G3) have transposon insertions (blue triangles) in genes encoding conserved components of the T6SS (grey arrows). The black dotted line represents intergenic sequence. (H) Mutants PMI0754::kan, 0755::kan, and 0758::kan merge with 9C1. (I) Killing assays confirming 9C1 killing are reported as [(CFU of test strain/CFU of 9C1)output]/[(CFU of test strain/CFU of 9C1)input]. Strain HI4230 kills mutant 9C1 by at least 7-logs. Mutant 9C1 complemented with the primary hcp-vgrG effector operon (9C1+) kills mutant 9C1. (J, K) Dienes line formation (arrows) was restored when the indicated mutants are complemented with the entire primary hcp-vgrG effector operon, (+); empty vector, (vc). (L) The 17 genes that encode the HI4320 T6SS are highly conserved with the well characterized T6SS genes from V. cholerae N16961 and have identical gene order in their respective chromosome and (M) comparison to the three known T6SSs (HSI-1, HSI-2, and HSI-3) encoded within the genome of P. aeruginosa PA01. The arrows are color-coded based upon known or predicted gene function. Black arrows represent genes that are not found in either P. mirabilis HI4320 or V. cholerae N16961 T6SS gene locus. See also Table S1.