Fig. 3.
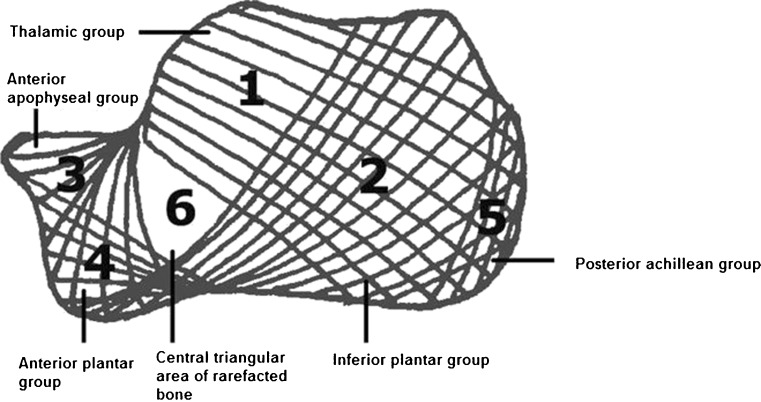
Calcaneal trabecular bone architecture. According to Diard et al. [7] the calcaneal trabecular bone architecture is described by six trabecular bone groups. In terms of functionality, the thalamic group (area 1) is the most important one, characterised by a trabeculation arising from the subchondral bone of the subtalar joint spreading on the cortex of the posterior tuberosity with a concave anteroinferior curve. The inferior plantar group (area 2) arises from the inferior cortex and spreads on the cortex of the posterior tuberosity with an anterosuperior curve. The anterior apophyseal group (area 3) is small and arises from the calcaneal cortex next to the tarsal sinus and spreads to the subchondral cortex of the anterior tuberosity. The anterior plantar group (area 4) is much reduced, spreading from the anterior part of the inferior cortex to the cortex of the anterior tuberosity. The posterior or achillean group (area 5) is parallel and close to the posterior cortex strengthening the posterior tuberosity. The first three major groups intertwine and delineate a central triangular radiolucent area (area 6) of rarefacted bone