Fig. 5.
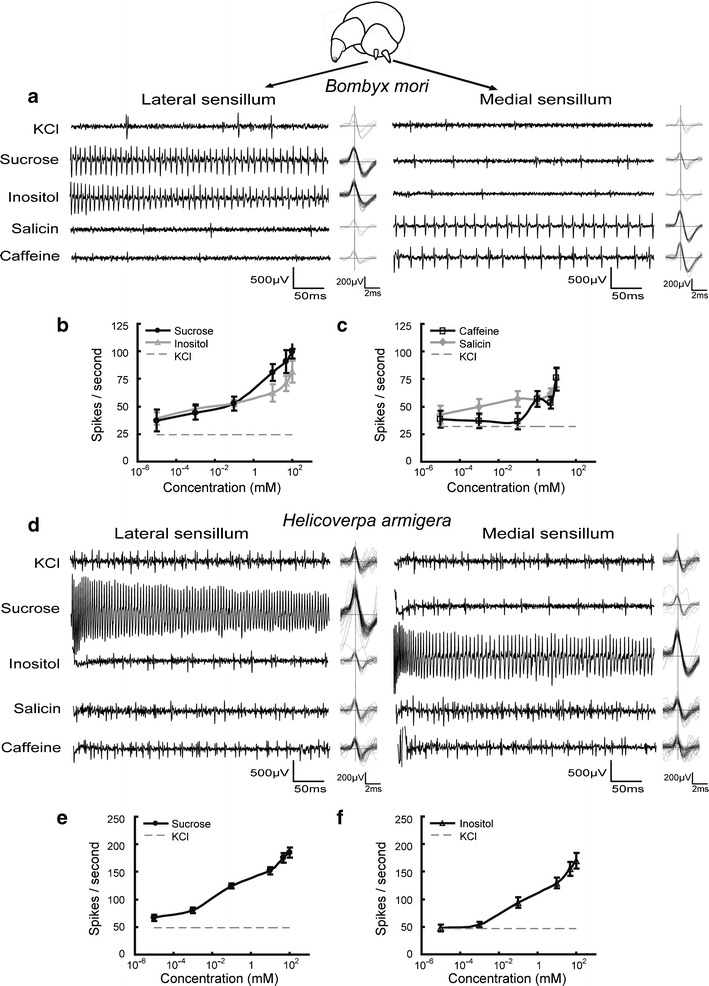
Electrophysiological responses of Bombyx mori and Helicoverpa armigera larval gustatory receptor neurons (GRNs) to bitter and sweet stimuli. a Examples of spike traces from B. mori styloconic sensilla over the first 500 ms of stimulation, with spike shape superimposition. b, c Concentration-dependence of GRN responses to sucrose and myo-inositol in the lateral styloconic sensillum (N = 13) and to salicin and caffeine in the medial styloconic sensillum (N = 10). d Examples of spike traces from H. armigera styloconic sensilla over the first 500 ms of stimulation, with spike shape superimposition. e, f Concentration-dependence of GRN responses to sucrose in the lateral styloconic sensilla of H. armigera to sucrose (N = 11) and to myo-inositol in the medial styloconic sensilla (N = 13). Chemical concentrations were as follows: KCl = 50 mM; sucrose = 100 mM; myo-inositol = 100 mM; salicin = 10 mM; and caffeine = 10 mM. Dotted lines indicate the GRN responses to 50 mM KCl and bars indicate the standard errors of the mean
