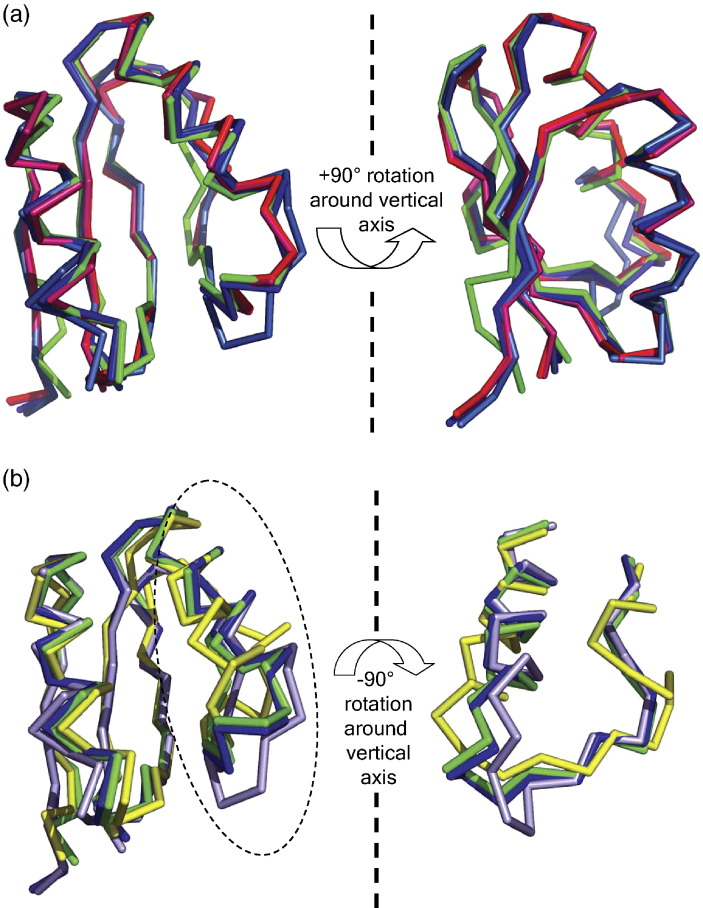
Figure 2.
Comparison of AYEdesign computational model and experimentally determined structures. (a) Both chains of AYEdes_VJQ (light and dark blue) and AYEdes (pink and red) are superimposed on the AYEdesign computational model (green), and are shown as Cα backbones in two orientations (related by a +90° rotation around the vertical axis in the plane of the page). The Cα RMSD from the computational model is 1.68 Å, 1.28 Å, 1.51 Å, and 1.51 Å for chain A and B of AYEdes_VJQ and AYEdes, respectively, and this improves to 1.13 Å, 0.65 Å, 1.05 Å and 1.05 Å, respectively, when 66 of the 70 residues are considered. (b) The two chains in AYEdes_VJQ (light and dark blue) differ notably from each other in the conformation of the loop containing residues 25–27. The backbone of AYEdes_VJQ chain B in this region is effectively superimposable with the AYEdesign computational model (green) as well as with the two chains of the AYEdes NMR structure, but the backbone of AYEdes_VJQ chain A deviates at this point. Interestingly, this corresponds to one of two points at which an insertion or deletion distinguishes the sequence families of procarboxypeptidase A (the template in this study) and procarboxypeptidase B; residues 25 and 26 are deleted from the procarboxypeptidase B sequence. The AYEdes_VJQ chain A backbone in the present structure does not, however, adopt the conformation of procarboxypeptidase B observed in PDB entry 1KWM (yellow), where the entire α-helix equivalent to residues 11–24 in the current sequence is displaced to one side.