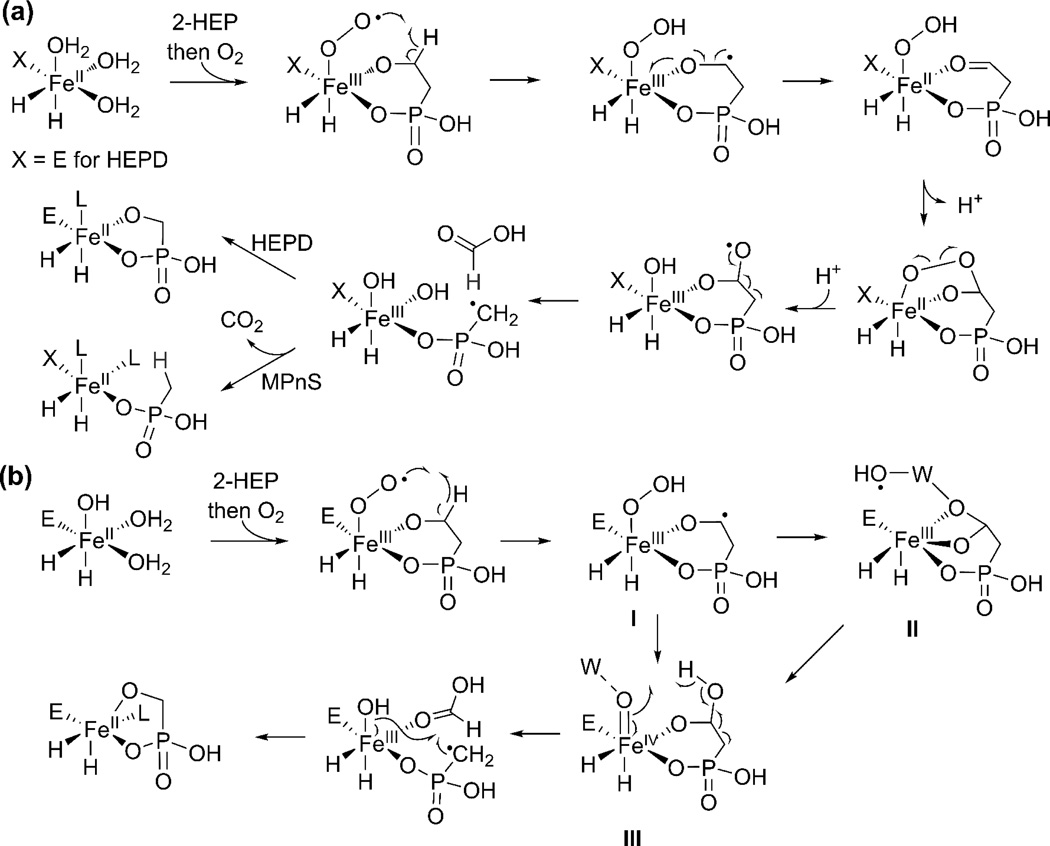
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of catalysis by the structurally-related enzymes HEPD and MPnS. (a) HEPD and MPnS are hypothesized to share a consensus mechanism that diverges only in the final step, with a radical rebound type hydroxylation for HEPD and hydrogen atom abstraction from formate for MPnS. (b) DFT calculations suggest that HEPD could proceed via an alternative mechanism that either indirectly (hydroperoxo intermediate I to radical II, and then to ferryl III) or directly (I to III) leads to a ferryl intermediate that abstracts a hydrogen atom from a hydroxyl group. A similar alternative mechanism with hydrogen atom abstraction from formate as the last step can also be drawn for MPnS. W is a water molecule; L is an unknown ligand.