Figure 4. Anal motor evoked potentials after transcranial magnetic stimulation.
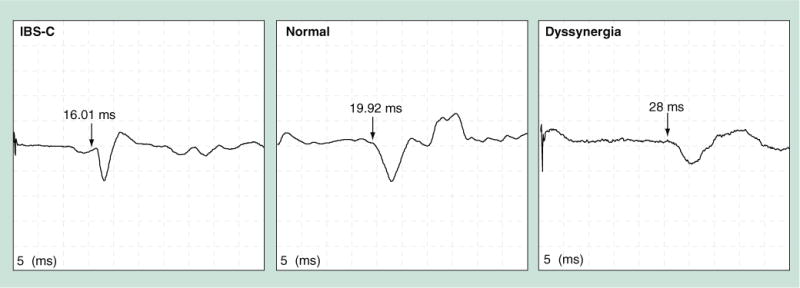
A patient with IBS-C has shorter latency whereas a subject with dyssynergea has prolonged latency of motor evoked potentials response compared with a normal subject. IBS-C: Predominant constipation irritable bowel syndrome.
