Figure 4. Effects of pharmacological blockers on the reciprocal and lateral IPSCs.
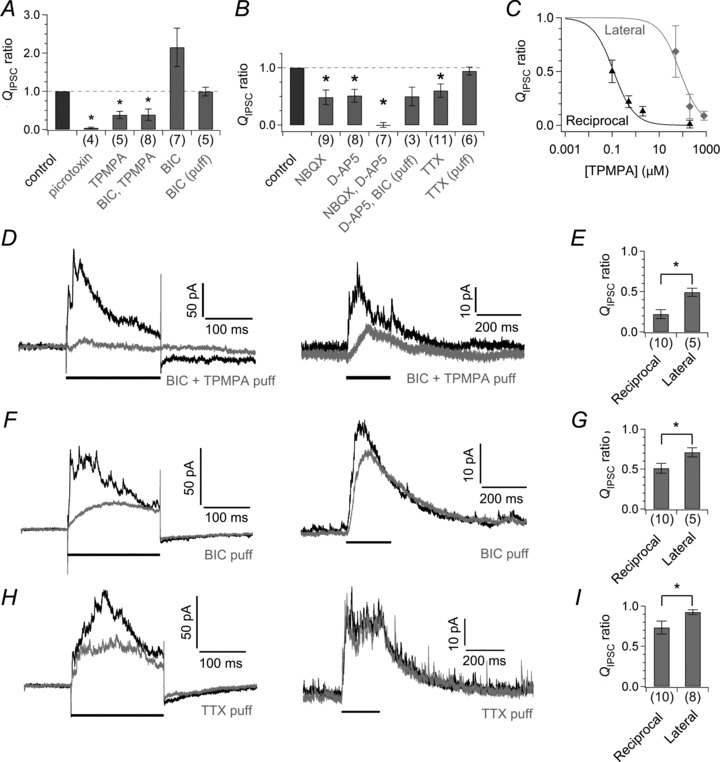
A and B, effects of various blockers on the lateral QIPSC/400 ms measured from axotomized terminals voltage clamped at −90 mV. Values are normalized to control (before the application of blockers). The asterisk indicates significant difference between before and during the application of blockers. C, dose (TPMPA)-dependent suppression of the reciprocal QIPSC (black triangle, n= 6–9) and the lateral QIPSC/200 ms measured from axotomized terminals voltage clamped at −90 mV (grey diamond, n= 3–5 pairs) in the presence of 100 μm BIC. Data were fitted to Hill functions. ID50 for the reciprocal QIPSC and lateral QIPSC is 0.12 μm and 76.02 μm, respectively. D and E, effects of a puff-applied mixture of BIC (100 μm) and TPMPA (20 μm) on the reciprocal IPSC (above) and the lateral IPSC (below) obtained under the same condition (D, see Methods). The reciprocal IPSC is shown as the difference between the averaged current response and the peak normalized ICa template for clarity. The horizontal bar indicates the period of the depolarizing pulse that elicited the reciprocal or lateral IPSC. Abscissa shows the ratio of QIPSC/200 ms under the puff application to that under control condition (E). The asterisk indicates significant interaction between the type of IPSC and the effect of puff-applied drug. F–I, effects of puff-applied 100 μm BIC (F and G) and puff-applied 1 μm TTX (H and I) on the reciprocal and lateral IPSCs as in D and E. BIC, bicuculline; d-AP5, d-(–)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid; NBQX, 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulphonamide; TPMPA, (1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) methylphosphinic acid; TTX, tetrodotoxin.
