Figure 7. A component of adenosine release is via equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs).
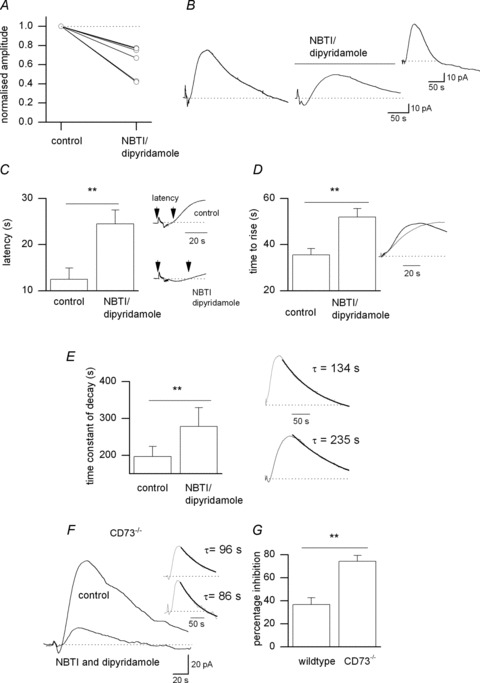
A, graph summarising the effects of NBTI (5 μm) and dipyridamole (10 μm) on the amplitude of the adenosine waveform (n= 7 slices). B, adenosine biosensor traces in control and in the presence of 5 μm NBTI and 10 μm dipyridamole. Inset, the NBTI/dipyridamole-sensitive current obtained by subtracting the trace in NBTI/dipyridamole from the control trace. C, graph summarising the effects of NBTI and dipyridamole on the latency of the adenosine waveform. The latency was measured as the time between the start of the stimulation and when the adenosine waveform started to rise above baseline. Inset, traces from B expanded to show the change in latency following application of NBTI and dipyridamole. D, graph summarising the effects of NBTI and dipyridamole on the rise time of the adenosine waveform. The rise time was measured as the time taken for the waveform to rise from the baseline to the peak. Inset, traces from B expanded and normalised to show slowing of rise following application of NBTI and dipyridamole (grey line). E, graph summarising the effects of NBTI and dipyridamole on the time constant of decay of the adenosine waveform. The decay was fitted with a single exponential. Inset, traces from B with the decay fitted with a single exponential. F, superimposed adenosine biosensor traces in control and in the presence of 5 μm NBTI and 10 μm dipyridamole in a recording from a CD73−/− mouse hippocampal slice. Inset, the traces from F normalised to illustrate that NBTI and dipyridamole had little effect on the kinetics of the waveform. G, graph summarising the effects of NBTI and dipyridamole on the stimulated increases in adenosine concentration detected in slices from wild-type and in CD73−/− mice. Graphs A, C, D and E all summarise data from seven slices. For G, n= 4 slices for wild-type mice and n= 6 slices for CD73−/− mice.
