Figure 7. Localization of CRF-R1 and RLN3-IR in the rat NI.
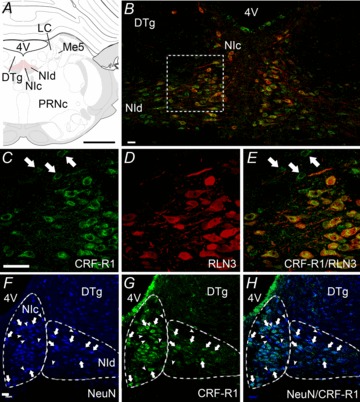
A, schematic depiction of the NI consisting of two midline columns of densely packed, large neurons (NIc) and more loosely distributed neurons located laterally (NId), which lie in the midline of the pontine central grey – ventral to the 4V and DTg, and medial to LC and Me5 (Paxinos & Watson 1998). B, cells of the NIc and NId are immunopositive for CRF-R1-IR (green) and RLN3-IR (red), though RLN3-IR is more prominently detected in NIc, whereas CRF-R1-IR is present in both NIc and NId (n= 5). All RLN3-IR cells contain CRF-R1-IR, but not all CRF-R1-IR cells contain RLN3-IR, particularly in the NId. C–E, higher magnification images of a region between the NIc and NId outlined in B. C, CRF-R1-IR appears as punctate, ring-like staining, indicative of labelling of membrane-bound receptor. D, in contrast, RLN3-IR is concentrated within the cytoplasm, proximal process and fibres, reflecting the synthesis, storage and trafficking of the peptide. E, merge of images B and C. Examples of CRF-R1-IR that did not co-localize with RLN3-IR are indicated by arrows in C and E. F–H, localization of CRF-R1 in NI neurons. F, strong NeuN-IR in NI neurons clearly delineates it from the DTg. G and H, all CRF-R1-IR was associated with NeuN-IR and clear examples are indicated by arrows. Some NeuN-IR neurons that were CRF-R1-negative are indicated by arrowheads. Images are confocal microscope single optical sections. Scale bars: A= 1.2 cm and B–H= 20 μm. CRF-R1, corticotrophin-releasing factor receptor-1; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus; 4V, fourth ventricle; IR, immunoreactivity; LC, locus coeruleus; Me5, mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve; NI, nucleus incertus; NIc, NI pars compacta; NId, NI pars dissipata; PRNc, caudal pontine reticular nucleus.
