Figure 9. Model of CRF-R1 localization and CRF actions in the NI.
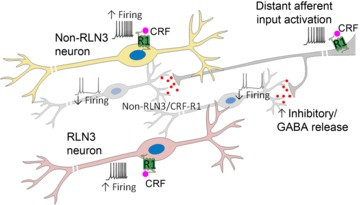
Schematic of a CRF-R1-positive neuron and CRF-R1/RLN3-positive neuron (foreground), which together constitute approximately half of the total NI neuronal population. In vivo and in vitro electrophysiological recordings suggest that these CRF-R1 and CRF-R1/RLN3 neurons are directly activated by CRF via postsynaptic CRF-R1, resulting in increased firing. Furthermore, a population of RLN3-negative cells (background) are inhibited by CRF in vivo, an effect not observed in vitro, suggesting that these neurons may receive an inhibitory input from a distant source activated by CRF, which is disconnected in a brain slice preparation. CRF, corticotrophin-releasing factor; CRF-R1, CRF receptor 1; NI, nucleus incertus.
