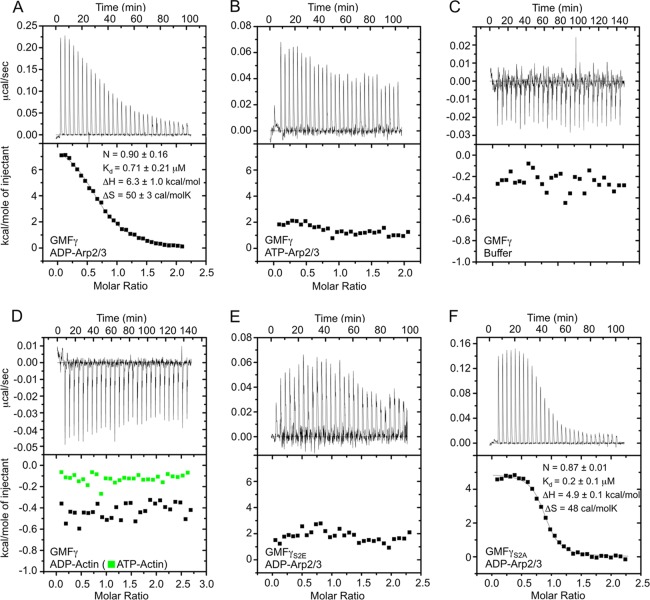
FIGURE 1.
Analysis by ITC of the binding of GMFγ to Arp2/3 complex. Experiments were conducted at 20 °C. Arp2/3 complex (or actin-latrunculin B) in the cell at 8–10 μm (or 13–15 μm) was titrated with a 14-fold molar excess of GMFγ in 7-μl injections (7-s injections, with an interval of 200 s between injections). A, titration of GMFγ into ADP-Arp2/3 complex. The data were fit to a binding isotherm derived from the integrated heats of binding plotted against the molar ratio of ligand (GMFγ) added to ADP-Arp2/3 complex in the cell after subtracting the heat of dilution. The best fit parameters (solid black line) correspond to a one-site binding model with a dissociation constant of 0.7 μm. B, titration of GMFγ into ATP-Arp2/3 complex. The data could not be fit to a binding isotherm. C, titration of GMFγ into buffer (control experiment). D, titration of GMFγ into ADP-actin (black squares) and ATP-actin (green squares). Note that these two titrations look similar to that of GMFγ into buffer, indicating a complete lack of interaction. E, titration of GMFγS2E into ADP-Arp2/3 complex. The data could not be fit to a binding isotherm. F, titration of GMFγS2A into ADP-Arp2/3 complex. Each titration was repeated at least two times, and four times for that shown in A. In A, errors are reported as S.E., whereas for the other titrations, errors were derived from curve fitting.