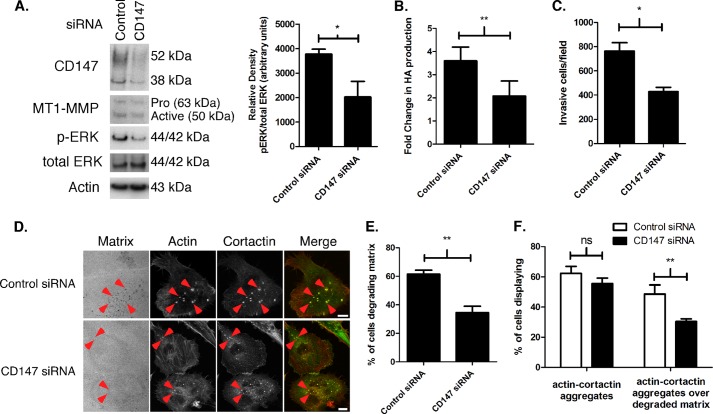
FIGURE 5.
Knockdown of CD147 in MCF-10 K-RasV12 cells results in decreased hyaluronan synthesis, MT1-MMP expression, ERK activation, and invasiveness. A, Western blot depicting CD147 and MT1-MMP protein levels and ERK phosphorylation in 10A-K-RasV12 cells depleted of CD147 by treatment with pooled siRNAs. Nonspecific siRNA was used as a control for CD147 knockdown, and β-actin was used as a loading control. Left, a representative gel. Right, densitometric quantitation of p-ERK versus total ERK. Columns, means ± S.E. (error bars); n = 3; *, p < 0.05. B, comparison of hyaluronan (HA) production in 10A-K-RasV12 cells treated with nonspecific control or pooled CD147-specific siRNA. Hyaluronan in the media was normalized to cell number and depicted as mean -fold change ± S.E.; each column represents three independent experiments; **, p < 0.01. C, quantitation of cell invasion through Matrigel by 10A-K-RasV12 cells treated with nonspecific control or pooled CD147-specific siRNA. Columns represent the mean number of invasive cells/field ± S.E.; n = 3; *, p < 0.05. D, representative micrographs demonstrating invadopodia in 10-K-RasV12 cells treated with nonspecific control or pooled CD147-specific siRNA cultured on fluorescent gelatin matrix. Red arrowheads, actin-cortactin aggregates. Scale bar, 10 μm. E, percentage of cells degrading underlying matrix or; F, percentage of cells with actin-cortactin aggregates with or without underlying degraded matrix in 10A-K-RasV12 cells treated with nonspecific control or pooled CD147-specific siRNA. Each invadopodia parameter was calculated by evaluating random fields containing at least 15 cells/field over three independent experiments. Column values are means ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01; ns, not significant.