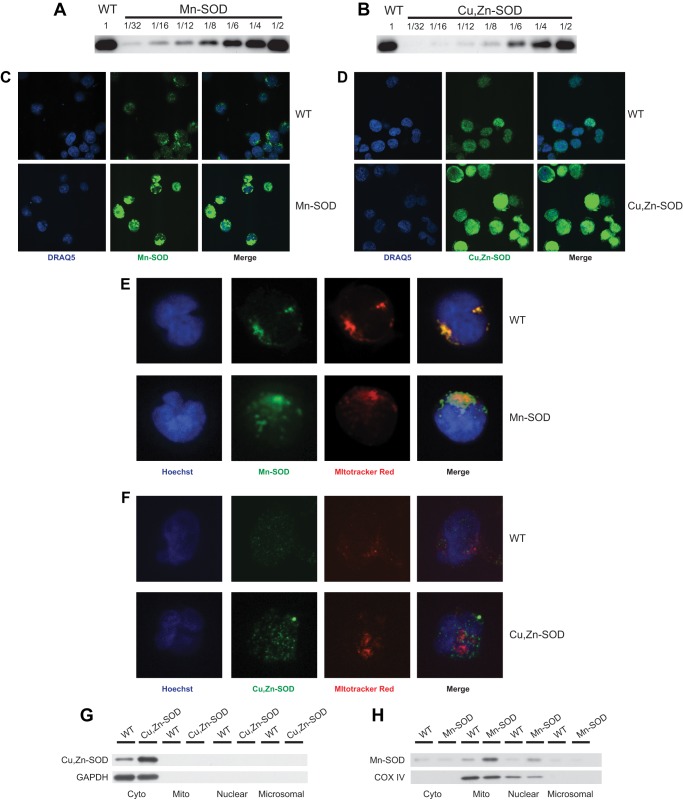
FIGURE 1.
Increased protein expression of Mn-SOD and Cu,Zn-SOD in transduced Jurkat cells. Immunoblot analysis was performed to determine the level of Mn-SOD (A) and Cu,Zn-SOD (B) protein expression in non-transduced Jurkat cells (WT) and Jurkat cells transduced by Mn-SOD and Cu,Zn-SOD, respectively. Serial dilutions of cell extracts isolated from transduced cells are shown in comparison to undiluted WT cell extract. WT and Jurkat cells transduced with Mn-SOD (C) and Cu,Zn-SOD (D) were stained with their respective antibodies and imaged by confocal microscopy. The relative florescence intensity of each overexpression line is greater than that of WT. Nuclei were stained with DRAQ. WT (upper panel) and Mn-SOD (E) or Cu,Zn-SOD (F) overexpressing (lower panel) Jurkat cells were stained with MitoTracker Red dye and Mn-SOD Ab or Cu,Zn-SOD Ab, respectively, followed by appropriate secondary Ab. The nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye, and the cells were imaged by confocal microscopy. Merging the images demonstrates mitochondrial specific localization of Mn-SOD, and that Cu,Zn-SOD does not localize to the mitochondria. Cytosolic, mitochondrial, nuclear, and microsomal fractions of WT and Cu,Zn-SOD (G) or Mn-SOD (H) transductants were isolated, fractionated by PAGE, and probed with Cu,Zn-SOD or Mn-SOD specific Abs, respectively. GAPDH, a cytosolic protein, or COX IV, a mitochondrial protein, were used both as localization and loading controls.