Figure 7.
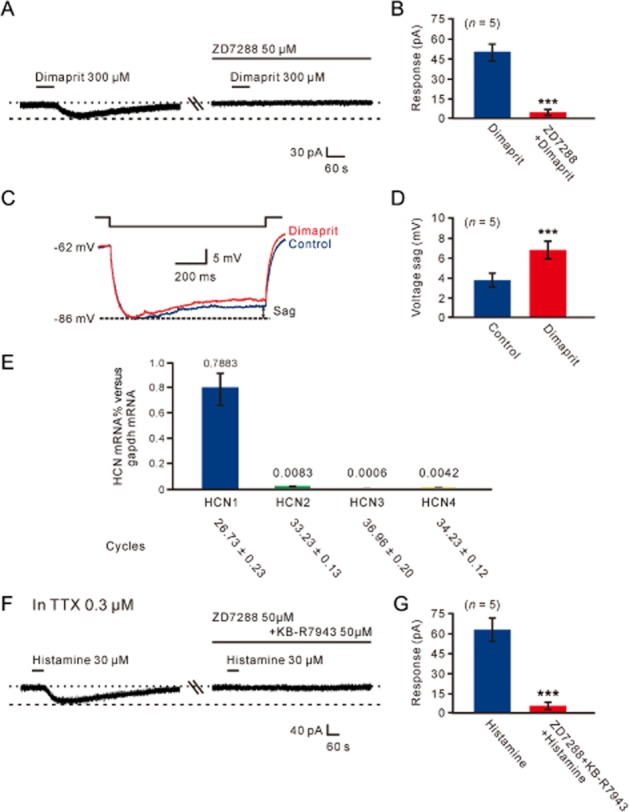
HCN channels mediated the histamine H2-receptor-induced inward current on MVN neurons. (A) ZD7288 totally blocked the inward current induced by dimaprit. (B) Group data of the five tested MVN neurons. Data shown are means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001. (C) Neuron displayed inward rectification (sag) in response to a hyperpolarizing current pulse. Dimaprit (300 μM) increased the amplitude of the voltage sag. (D) Group data of the depolarizing sag of the five tested MVN neurons in the absence and presence of dimaprit. Data shown are means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001. (E) Bar graphs showing relative expression of HCN1, HCN2, HCN3 and HCN4 channel mRNAs in the MVN. (F) In the presence of TTX, combined application of ZD7288 and KB-R7943 totally blocked the histamine-induced postsynaptic inward current, indicating HCN channels and NCXs co-mediate the postsynaptic excitatory effect of histamine on MVN neurons. (G) Group data of the five tested MVN neurons. Data shown are means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001.
