Table 1.
Different types of drug delivery system.
| Drug delivery system | Structure | Chemical properties | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes |  |
Consists of hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head group | 27–29 |
| Forms closed vesicles with an aqueous core | |||
| Internal aqueous domain between the lipid bilayers | |||
| Encapsulation of drugs occurs either in the aqueous space or intercalated into the bilayer | |||
| Dendrimers | 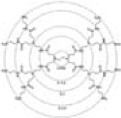 |
Hyper branched and globular macromolecules | 30–32 |
| Well defined core, backbone and multivalent periphery | |||
| By hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, incorporate biomolecules | |||
| Convergent – endo-receptor | |||
| Divergent – exo-receptor | |||
| Carbon nanotubes | 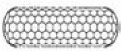 |
Rolling up a single layer of grapheme sheet – single walled | 33–37 |
| Rolling up many layers to form concentric cylinders – multi-walled | |||
| Gold nanoparticles |  |
Gold nanoparticle serves as core | 8,38 |
| Photosensitive | |||
| Iron oxide nanoparticles |  |
Superparamagnetic particles | 8,39 |
| Need trigger to release biomolecules, for example, laser irradiation | |||
| Titanium dioxide nanoparticles |  |
Self-ordered | 40–42 |
| Nano-tubular structure | |||
| Photodynamic therapy | |||
| Silica nanoparticles |  |
Mesoporous structure | 7, 23, 25 |
| Honeycomb-like structure | |||
| Active surface |
