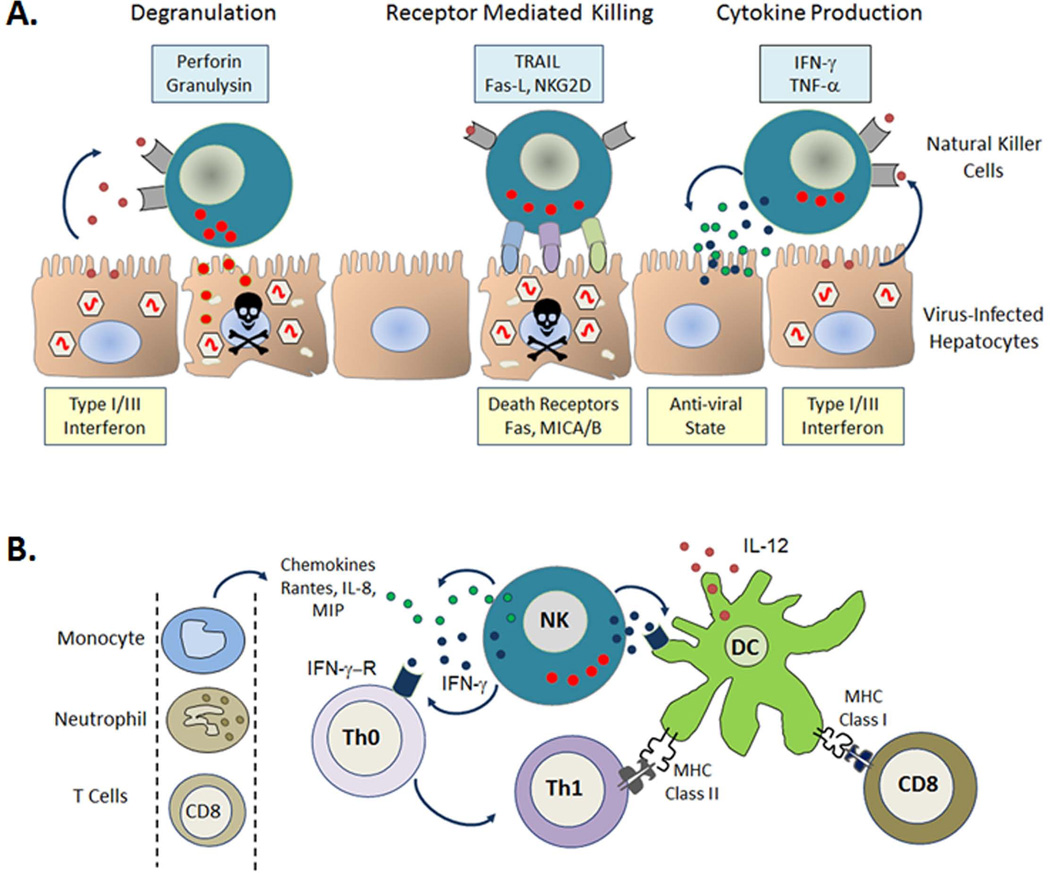
Fig. 2. Direct and indirect anti-viral effector mechanisms of natural killer (NK) cells.
In the setting of viral infection, infected cells produce Type I/III interferon (IFN). NK cells respond through direct mechanisms; degranulation and receptor mediated lysis of infected cells as well as production of anti-viral cytokines such as IFN-γ (A). NK cells also act indirectly to prime the adaptive immune response promoting dendritic cell (DC) maturation and the differentiation of immature helper T cells (Th0) towards an inflammatory phenotype (Th1). Production of chemokines by NK cells attracts other immune cells to sites of inflammation (B). TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Fas-L, Fas ligand; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IFN-γ-R, interferon-γ receptor; IL-8/12, interleukin-8/12; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; MHC, major histocompatibility complex.