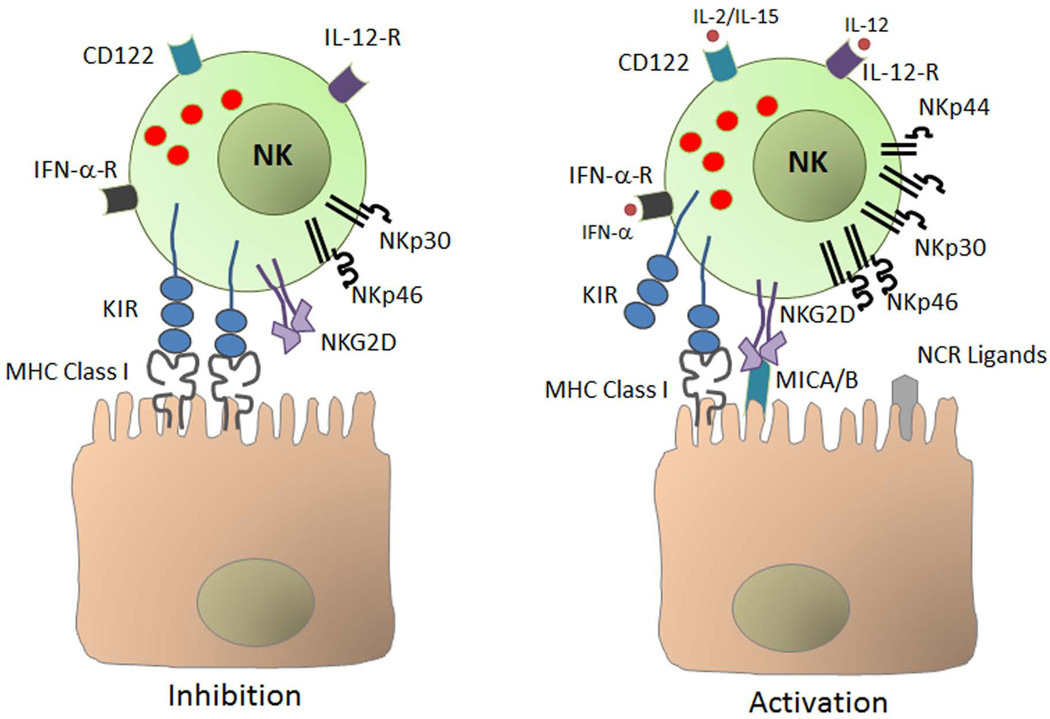
Fig. 3. Activation of natural killer (NK) cells.
Under normal conditions, NK cells are constitutively inhibited mainly through engagement of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules on normal cells by NK cell-expressed killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR). Under conditions of stress such as viral infection, loss of constitutive inhibition through downregulation of MHC class I, upregulation of activating receptors and/or their ligands, cell adhesion, and response to inflammatory cytokines including interferon-α (IFN-α) and interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-12, and IL-15 results in activation of NK cells. MICA/B, MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A/B; NCR, natural cytotoxicity receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IFN-α-R, IFN-α receptor.