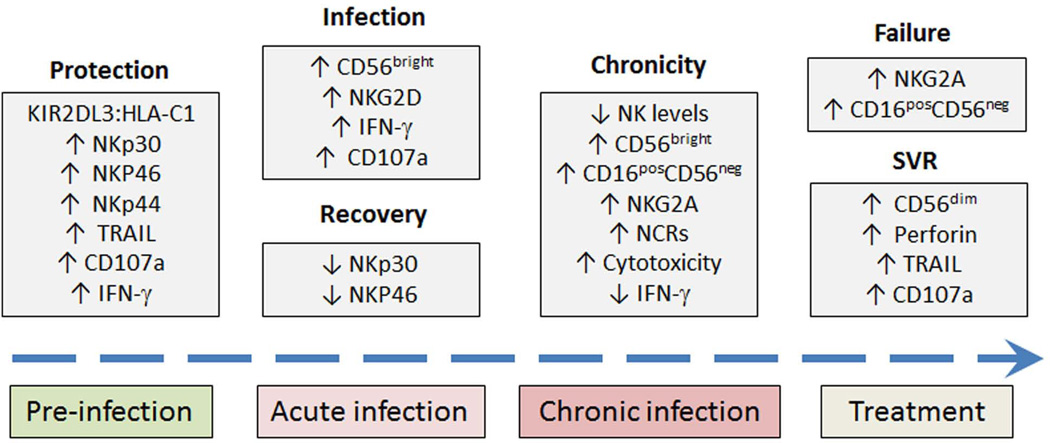
Fig. 5. Natural killer (NK) cells play important roles in every stage of HCV infection.
NK cells play important roles in every stage of HCV infection from protection against infection in IDUs to prediction of antiviral success or failure with IFN-based therapies. Several NKRs and functional properties of NK cells have been implicated. Their association with natural history, stage of infection and treatment outcome are shown. KIR, killer immunoglobulin-like receptor; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; NCRs, natural cytotoxicity receptors; SVR, sustained virological response.