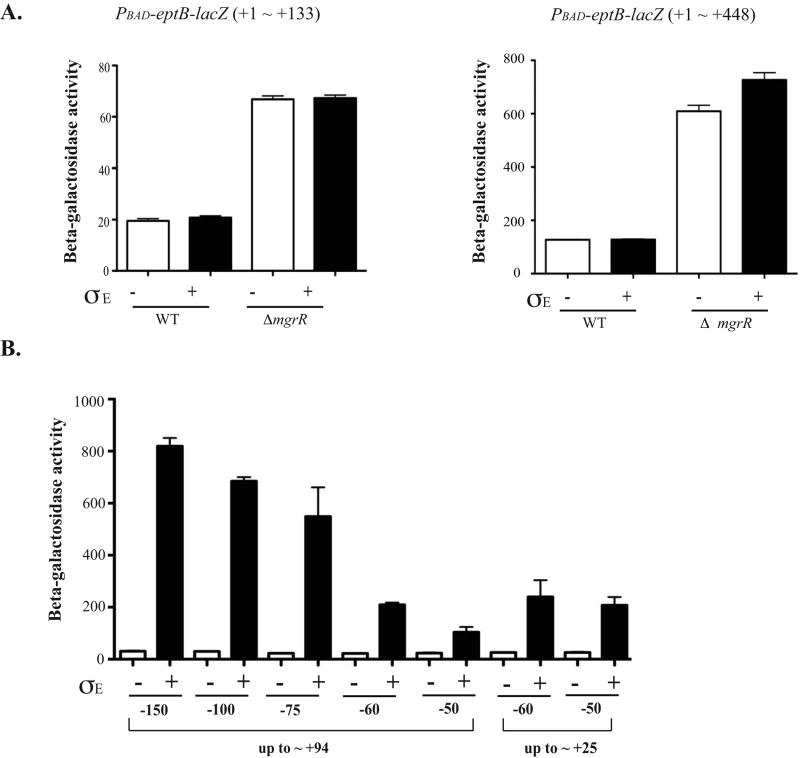
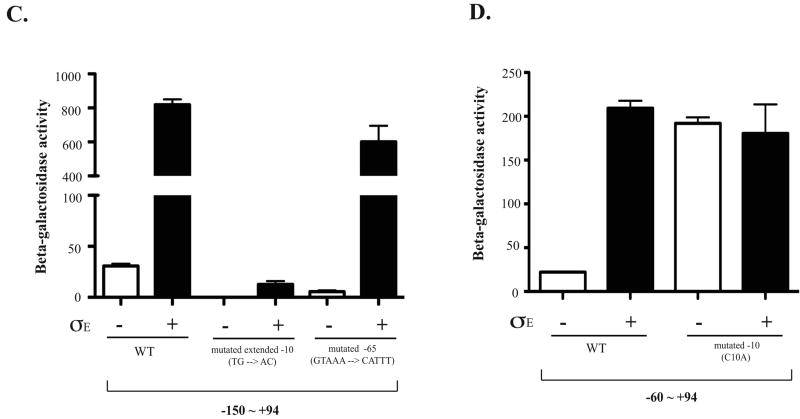
Figure 6. Regulation of eptB by sigma E.
A. Two different translational fusions of eptB were constructed; each is expressed from an arabinose inducible promoter (PBAD). One (KM125) contains from +1 to +133 of the eptB mRNA, which includes the sequence encoding 9 amino acids of eptB and the other one contains from +1 to +448 (KM233); this should be similar to the fusion used by Figueroa-Bossi et al (Figueroa-Bossi et al., 2006), but with the promoter exchanged. Cells containing either a control vector or a vector harboring Sigma E under the inducible promoter (Ptec) were inoculated in LB with ampicillin and a final concentration of 100 uM of IPTG and 0.2% arabinose. The cells were collected at 5 hours (OD600 = 1∼2). The Miller assay was performed to measure the activity of β-galactosidase in both WT and mgrR deletion backgrounds. The results reported are representative of at least three experimental trials. Error bars indicate standard deviations. B. Various upstream regions of eptB promoter fusions were constructed to examine the effect of Sigma E. Also, two different lengths of the DNA downstream of +1 were used to characterize the minimal promoter element for the regulation, +25 and +94. Cells were grown for 5 hours to reach the stationary phase in the presence of IPTG with either the control vector or the Sigma E plasmid and collected for a Miller assay to measure the enzyme activity. The results reported are representative of four independent experimental trials and standard deviations are shown as error bars. C. Cells were grown and assayed as for A and B. A possible extended -10 (TG→AC) (KM250) and GTAAA box located at -65 were mutated in the background of KM 238 (-150 ∼ +94) (KM299). The wild-type data are the same as for panel B. D. Cells were grown and assayed as for A and B. The -10 mutation (C→A) (KM202-1) was an inadvertant change identified during screening of various fusions and saved. It is compared to its wild-type sibling (KM202-3), also shown in Fig. 6B.