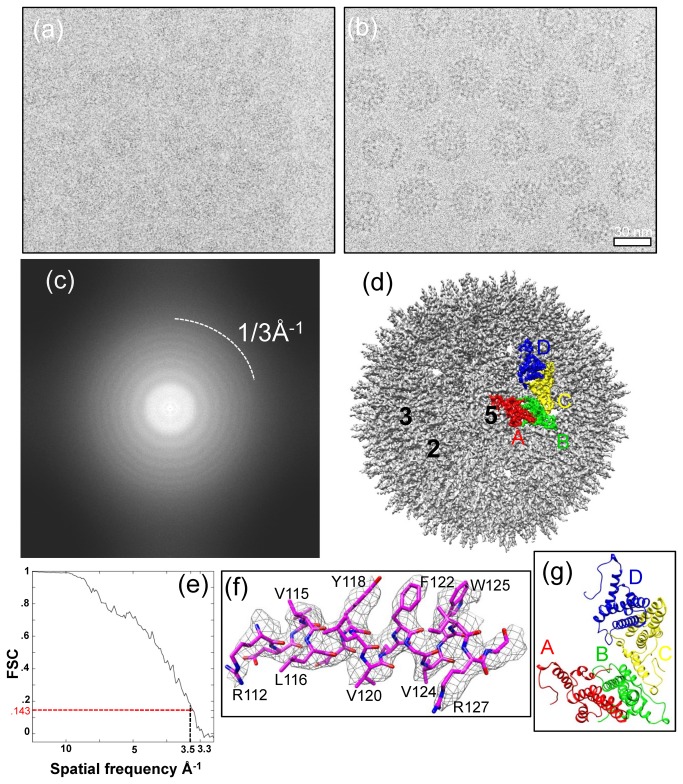
Figure 1. CryoEM and 3D reconstruction of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core assembled from full-length HBV core proteins at 3.5Å resolution.
(a, b) Representative focal-pair cryoEM images of core particles embedded in a thin layer of vitreous ice, recorded on Kodak So 163 film in an FEI Titan Krios cryo electron microscope operated at 300kV at liquid-nitrogen temperature. (c) Fourier transform of the cryoEM image in (a), showing contrast transfer function rings visible up to 1/3Å-1. (d) Shaded surface representation of the core reconstruction at 3.5Å resolution as viewed along a five-fold axis. One asymmetric unit is segmented and color-coded. The A, B, C, and D subunits that form the asymmetric unit are colored in red, green, yellow, and blue, respectively. The two-fold, three-fold, and five-fold axes are indicated by the numbers 2, 3, and 5, respectively. (e) Resolution assessment of HBV 3D reconstruction based on the 0.143 criterion of reference-based Fourier shell correlation coefficient, showing that the effective resolution is ~3.5Å. (f) Atomic model (stick) of an α-helix is superimposed in its density map (mesh). (g) An atomic model of an asymmetric unit of the T=4 HBV core derived from the cryoEM structure viewed along a five-fold axis. The A, B, C, and D subunits that form the asymmetric unit are color-coded in red, green, yellow, and blue, respectively.