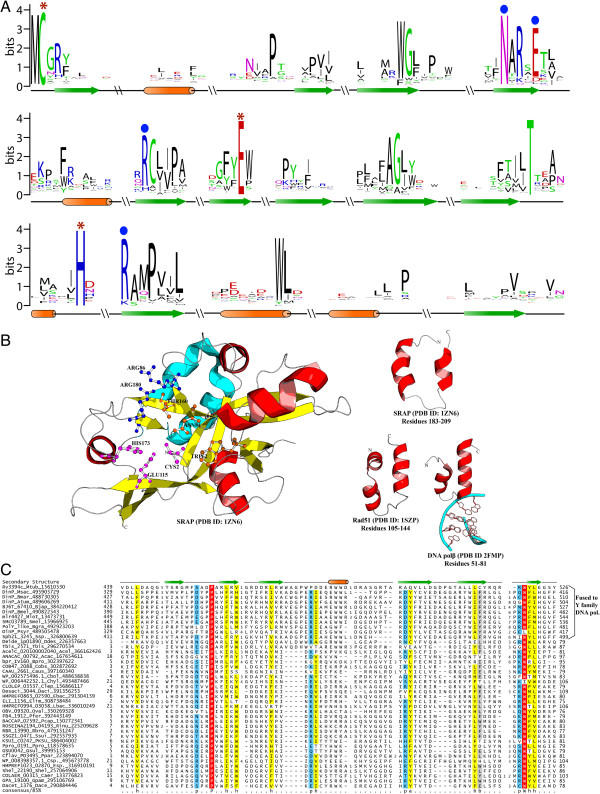
Figure 2.
Sequence conservation of the SRAP and ImuB-C domains, and structure of the SRAP domain. A) Sequence logo for SRAP domain obtained from a multiple sequence alignments of representative sequences (See Additional file 1 for complete alignment). Residues predicted to catalyze auto-proteolysis are marked with red asterisks. Other conserved residues described in the text are marked with blue circles. B) A cartoon representation of the predicted active site for the SRAP protein is shown in left panel. The catalytic triad comprising of Cys2, His173 and E115 (PDB: 1zn6) has been depicted in magenta color, the arginine residues predicted to interact with DNA are shown in dark blue color, while the other conserved residues in active site are shown in orange. The predicted Helix-hairpin helix (HhH) region of SRAP domain (cyan) is shown in the right panel separately along with the HhH domains of RecA and the DNA polymerase β for comparison. C) Multiple sequence alignment of the ImuB-C domain. Proteins are labeled to the left of each sequence by their gene names, species abbreviations, and gi numbers separated by underscores. Amino acid residues are colored according to side chain properties and degree of conservation within the alignment, at 85% consensus. The secondary structure is indicated above the alignment with helices shown as orange cylinders and strands as green arrows. The consensus abbreviations and coloring scheme are as follows: h, hydrophobic (ACFGHILMTVWY) and a: aromatic (FYH) residues shaded yellow; polar (CDEHKNQRST) residues colored blue; big residues (QRKEILMWYF) shaded grey; absolutely conserved residues shaded red. Species abbreviations are provided in Additional file 1.