Table 2. Representative parameters of physiological factors underlying mobility for each age group.
| Y | M | O | |
| (n = 24) | (n = 24) | (n = 24) | |
| T vent | |||
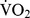 (ml kg–1 min–1) (ml kg–1 min–1) |
27.0±5.0* ‡ | 22.7±6.1† | 16.0±2.8 |
| HR (beats min–1) | 141.4±14.0* | 143.2±13.1† | 116.0±14.0 |
| Load (W) | 130.8±25.7* | 126.2±42.0† | 74.7±17.8 |
| MVC | |||
| Peak torque (N m kg–1) | 2.46±0.68* ‡ | 1.91±0.58 | 1.55±0.47 |
| RFD (N m s–1) | 1095.0±328.2* | 1007.9±311.5 | 855.4±270.3 |
| CMJ | |||
| Flight time (s) | 0.47±0.06* ‡ | 0.38±0.07† | 0.30±0.06 |
| V-peak power (W kg–1) | 52.0±14.7* | 47.9±22.2† | 24.7±5.9 |
| STS | |||
| V-peak power (W kg–1) | 16.4±4.2* ‡ | 12.7±3.4 | 10.5±3.7 |
| AP-peak power (W kg–1) | 1.55±0.65* | 1.20±0.53 | 1.02±0.43 |
| sEMG | |||
| MFCV (m s−1) | 4.43±0.47 | 4.06±0.67 | 4.31±0.57 |
| Coactivation (%) | 29.6±20.5 | 31.7±22.5 | 26.2±22.8 |
Values are means ± SD of the following mobility parameters: oxygen consumption (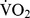 ), heart rate (HR), and mechanical load at ventilatory threshold (Tvent) during incremental cycling; vertical (V) and antero-posterior (AP) peak power during chair rising (STS) at maximal intensity; flight time and peak power during a countermovement jump (CMJ); peak torque and rate of force development (RFD) during isometric maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) of knee extensor muscles; muscle fiber conduction velocity (MFCV) of vastus lateralis and the antagonist coactivation from surface electromyography (sEMG) during knee extension maximal voluntary contraction.
), heart rate (HR), and mechanical load at ventilatory threshold (Tvent) during incremental cycling; vertical (V) and antero-posterior (AP) peak power during chair rising (STS) at maximal intensity; flight time and peak power during a countermovement jump (CMJ); peak torque and rate of force development (RFD) during isometric maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) of knee extensor muscles; muscle fiber conduction velocity (MFCV) of vastus lateralis and the antagonist coactivation from surface electromyography (sEMG) during knee extension maximal voluntary contraction.
= significantly different between young (Y) and older (O) participants;
= significantly different between middle-aged (M) and older participants;
significantly different between young and middle-aged participants.
