Figure 5.
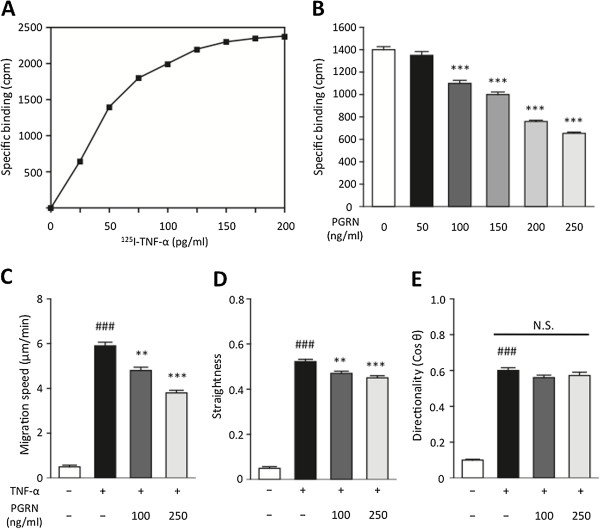
PGRN inhibits 125I-TNF-α binding to neutrophil surfaces and suppresses neutrophil chemotaxis induced by TNF-α. (A) Saturation curve for specific 125I-TNF-α binding to neutrophil surfaces was determined, and in accordance with these results, 50 pg/mL of 125I-TNF-α was used in the subsequent experiments. (B) The 125I-TNF-α binding significantly decreased with increasing concentrations of PGRN. ***P <0.001 vs. 0 ng/mL of PGRN group; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. Data were obtained from three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. (C, D, E) Neutrophil chemotaxis was induced by TNF-α, and PGRN was found to significantly suppress this effect in a concentration-dependent manner; at 100 and 250 ng/mL of PGRN attenuates the migration speed and straightness of the route of migration, but did not affect the directionality of migration. ### P <0.001 vs. control group; Student t-test; ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 vs. TNF-α only group; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test; n = 5 for each group. PGRN, progranulin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
