Figure 7.
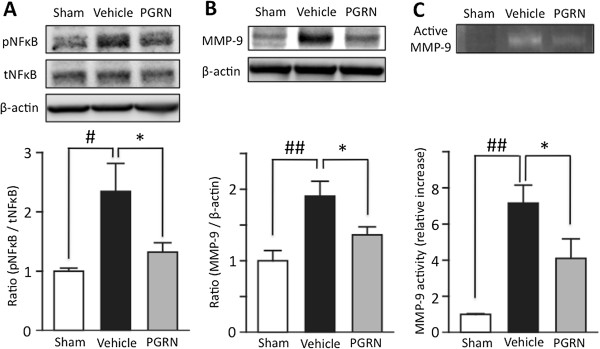
PGRN significantly suppresses the expression of MMP-9, and the phosphorylation of NF-κB in I/R brain. (A) Representative bands from Western blotting analysis of phosphorylated and total NF-κB (upper). Optical densitometry quantification for the phosphorylation of NF-κB (p NF-κB), normalized to total NF-κB (tNF-κB) and β-actin (lower). In the I/R brain, phosphorylation of NF-κB was significantly increased. ## P <0.01 vs. sham control group; Student's t-test. PGRN significantly suppressed this increased phosphorylation of NF-κB induced by I/R. * P <0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group; Student t-test. (B) Representative bands from Western blotting analysis of MMP-9 expression (upper). Optical densitometry quantification of MMP-9 expression, normalized to β-actin (lower). MMP-9 expression was significantly increased in the I/R brain. ## P <0.01 vs. sham control group; Student's t-test. PGRN significantly suppressed the expression of MMP-9 induced by I/R. * P <0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group; Student's t-test; n = 5 for each group. (C) Representative bands from gelatin zymography for activated MMP-9 (upper). Optical densitometry quantification of activated MMP-9 (lower). Activated MMP-9 was significantly increased in the I/R brain. ## P <0.01 vs. sham control group; Student's t-test. PGRN significantly suppressed the activation of MMP-9 induced by I/R. * P <0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group; Student's t-test; n = 3 for sham or n = 4 for each treated group. I/R, ischemia-reperfusion; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κappaB; PGRN, progranulin.
