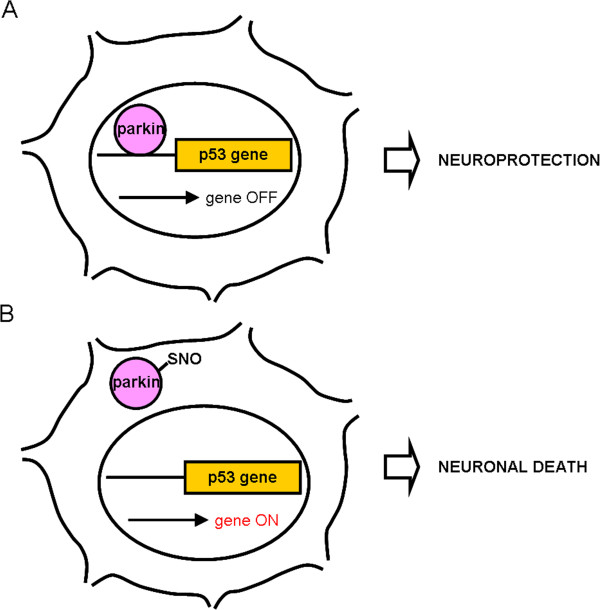
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of proposed mechanism whereby S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates p53-mediated neuronal death in sporadic PD. A, Under physiological conditions, parkin is neuroprotective by repressing p53 transcription. B, During nitrosative stress, for example due to pesticide exposure, parkin becomes S-nitrosylated. SNO-parkin no longer binds to the p53 promoter and is excluded from the nucleus. This results in activation of the p53 gene and subsequent p53-mediated neuronal death.